A 3D human brain-like tissue model of herpes-induced Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 32494701
- PMCID: PMC7202879
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aay8828
A 3D human brain-like tissue model of herpes-induced Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
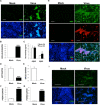
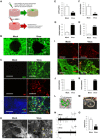
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that causes cognitive decline, memory loss, and inability to perform everyday functions. Hallmark features of AD-including generation of amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, gliosis, and inflammation in the brain-are well defined; however, the cause of the disease remains elusive. Growing evidence implicates pathogens in AD development, with herpes simplex virus type I (HSV-1) gaining increasing attention as a potential causative agent. Here, we describe a multidisciplinary approach to produce physiologically relevant human tissues to study AD using human-induced neural stem cells (hiNSCs) and HSV-1 infection in a 3D bioengineered brain model. We report a herpes-induced tissue model of AD that mimics human disease with multicellular amyloid plaque-like formations, gliosis, neuroinflammation, and decreased functionality, completely in the absence of any exogenous mediators of AD. This model will allow for future studies to identify potential downstream drug targets for treating this devastating disease.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures



References
-
- Alzheimer's Association , 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 12, 459–509 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Weyer S. W., Klevanski M., Delekate A., Voikar V., Aydin D., Hick M., Filippov M., Drost N., Schaller K. L., Saar M., Vogt M. A., Gass P., Samanta A., Jäschke A., Korte M., Wolfer D. P., Caldwell J. H., Müller U. C., APP and APLP2 are essential at PNS and CNS synapses for transmission, spatial learning and LTP. EMBO J. 30, 2266–2280 (2011). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

