Life cycle of a cyanobacterial carboxysome
- PMID: 32494723
- PMCID: PMC7202890
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba1269
Life cycle of a cyanobacterial carboxysome
Abstract
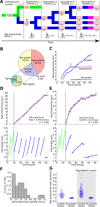
Carboxysomes, prototypical bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) found in cyanobacteria, are large (~1 GDa) and essential protein complexes that enhance CO2 fixation. While carboxysome biogenesis has been elucidated, the activity dynamics, lifetime, and degradation of these structures have not been investigated, owing to the inability of tracking individual BMCs over time in vivo. We have developed a fluorescence-imaging platform to simultaneously measure carboxysome number, position, and activity over time in a growing cyanobacterial population, allowing individual carboxysomes to be clustered on the basis of activity and spatial dynamics. We have demonstrated both BMC degradation, characterized by abrupt activity loss followed by polar recruitment of the deactivated complex, and a subclass of ultraproductive carboxysomes. Together, our results reveal the BMC life cycle after biogenesis and describe the first method for measuring activity of single BMCs in vivo.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures



References
-
- Turmo A., Gonzalez-Esquer C. R., Kerfeld C. A., Carboxysomes: Metabolic modules for CO2 fixation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 364, fnx176 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Price G. D., Badger M. R., Evidence for the role of carboxysomes in the cyanobacterial CO2 -concentrating mechanism. Can. J. Bot. 69, 963–973 (1991).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

