A Novel Aortic Regurgitation Model from Cusp Prolapse with Hemodynamic Validation Using an Ex Vivo Left Heart Simulator
- PMID: 32495264
- PMCID: PMC8362820
- DOI: 10.1007/s12265-020-10038-z
A Novel Aortic Regurgitation Model from Cusp Prolapse with Hemodynamic Validation Using an Ex Vivo Left Heart Simulator
Abstract
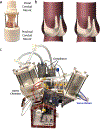
Although ex vivo simulation is a valuable tool for surgical optimization, a disease model that mimics human aortic regurgitation (AR) from cusp prolapse is needed to accurately examine valve biomechanics. To simulate AR, four porcine aortic valves were explanted, and the commissure between the two largest leaflets was detached and re-implanted 5 mm lower to induce cusp prolapse. Four additional valves were tested in their native state as controls. All valves were tested in a heart simulator while hemodynamics, high-speed videography, and echocardiography data were collected. Our AR model successfully reproduced cusp prolapse with significant increase in regurgitant volume compared with that of the controls (23.2 ± 8.9 versus 2.8 ± 1.6 ml, p = 0.017). Hemodynamics data confirmed the simulation of physiologic disease conditions. Echocardiography and color flow mapping demonstrated the presence of mild to moderate eccentric regurgitation in our AR model. This novel AR model has enormous potential in the evaluation of valve biomechanics and surgical repair techniques. Graphical Abstract.
Keywords: Aortic regurgitation; Cusp prolapse; Left heart simulator; Porcine model.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Roberts WC, Ko JM (2005) Frequency by Decades of Unicuspid, Bicuspid, and Tricuspid Aortic Valves in Adults Having Isolated Aortic Valve Replacement for Aortic Stenosis, With or Without Associated Aortic Regurgitation. Circulation 111(7):920–925. - PubMed
-
- Akinseye OA, Pathak A, Ibebuogu UN (2018) Aortic Valve Regurgitation: A Comprehensive Review. Curr Probl Cardiol 43(8):315–334. - PubMed
-
- Elkhoury G (2004) Repair of aortic valve prolapse: experience with 44 patients. Eur J Cardio-Thoracic Surg 26(3):628–633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

