Genome editing enables reverse genetics of multicellular development in the choanoflagellate Salpingoeca rosetta
- PMID: 32496191
- PMCID: PMC7314544
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.56193
Genome editing enables reverse genetics of multicellular development in the choanoflagellate Salpingoeca rosetta
Abstract
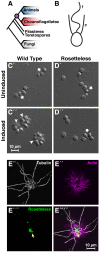
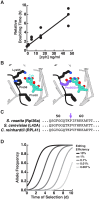
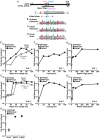
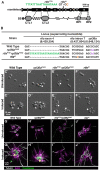
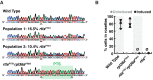
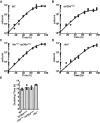
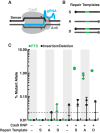
In a previous study, we established a forward genetic screen to identify genes required for multicellular development in the choanoflagellate, Salpingoeca rosetta (Levin et al., 2014). Yet, the paucity of reverse genetic tools for choanoflagellates has hampered direct tests of gene function and impeded the establishment of choanoflagellates as a model for reconstructing the origin of their closest living relatives, the animals. Here we establish CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in S. rosetta by engineering a selectable marker to enrich for edited cells. We then use genome editing to disrupt the coding sequence of a S. rosetta C-type lectin gene, rosetteless, and thereby demonstrate its necessity for multicellular rosette development. This work advances S. rosetta as a model system in which to investigate how genes identified from genetic screens and genomic surveys function in choanoflagellates and evolved as critical regulators of animal biology.
Keywords: Salpingoeca rosetta; choanoflagellates; developmental biology; genetics; genome editing; genomics; multicellularity.
© 2020, Booth and King.
Conflict of interest statement
DB, NK No competing interests declared
Figures
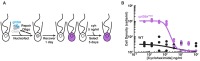

Similar articles
-
The Rosetteless gene controls development in the choanoflagellate S. rosetta.Elife. 2014 Oct 9;3:e04070. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04070. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25299189 Free PMC article.
-
The history of Salpingoeca rosetta as a model for reconstructing animal origins.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2022;147:73-91. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2022.01.001. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35337467
-
Forward genetics for back-in-time questions.Elife. 2014 Nov 4;3:e05218. doi: 10.7554/eLife.05218. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25369637 Free PMC article.
-
Choanoflagellate models - Monosiga brevicollis and Salpingoeca rosetta.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Aug;39:42-47. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.05.016. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 27318693 Review.
-
Selective factors in the evolution of multicellularity in choanoflagellates.J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2021 Apr;336(3):315-326. doi: 10.1002/jez.b.22941. Epub 2020 Mar 21. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol. 2021. PMID: 32198827 Review.
Cited by
-
Three-dimensional flagella structures from animals' closest unicellular relatives, the Choanoflagellates.Elife. 2022 Nov 17;11:e78133. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78133. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36384644 Free PMC article.
-
An RFX transcription factor regulates ciliogenesis in the closest living relatives of animals.Curr Biol. 2023 Sep 11;33(17):3747-3758.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.07.022. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Curr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37552984 Free PMC article.
-
Assembling a Hippo: the evolutionary emergence of an animal developmental signaling pathway.Trends Biochem Sci. 2024 Aug;49(8):681-692. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2024.04.005. Epub 2024 May 9. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38729842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-induced disruption of Bodo saltans paraflagellar rod-2 gene reveals its importance for cell survival.Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jul;24(7):3051-3062. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15918. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35099107 Free PMC article.
-
Cell differentiation controls iron assimilation in the choanoflagellate Salpingoeca rosetta.mSphere. 2025 Mar 25;10(3):e0091724. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00917-24. Epub 2025 Feb 26. mSphere. 2025. PMID: 40008892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afgan E, Baker D, Batut B, van den Beek M, Bouvier D, Cech M, Chilton J, Clements D, Coraor N, Grüning BA, Guerler A, Hillman-Jackson J, Hiltemann S, Jalili V, Rasche H, Soranzo N, Goecks J, Taylor J, Nekrutenko A, Blankenberg D. The galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2018;46:W537–W544. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

