Evaluation of multi-antigen serological screening for active tuberculosis among people living with HIV
- PMID: 32497095
- PMCID: PMC7272080
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234130
Evaluation of multi-antigen serological screening for active tuberculosis among people living with HIV
Abstract
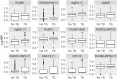
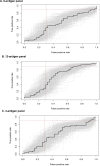
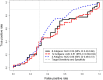
Better triage tests for screening tuberculosis (TB) disease are needed for people living with HIV (PLHIV). We performed the first evaluation of a previously-validated 8-antigen serological panel to screen PLHIV for pulmonary TB in Kampala, Uganda. We selected a random 1:1 sample with and without TB (defined by sputum culture) from a cohort of PLHIV initiating antiretroviral therapy. We used a multiplex microbead immunoassay and an ensemble machine learning classifier to determine the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for Ag85A, Ag85B, Ag85C, Rv0934-P38, Rv3881, Rv3841-BfrB, Rv3873, and Rv2878c. We then assessed the performance with the addition of four TB-specific antigens ESAT-6, CFP-10, Rv1980-MPT64, and Rv2031-HSPX, and every antigen combination. Of 262 participants (median CD4 cell-count 152 cells/μL [IQR 65-279]), 138 (53%) had culture-confirmed TB. The 8-antigen panel had an AUC of 0.53 (95% CI 0.40-0.66), and the additional 4 antigens did not improve performance (AUC 0.51, 95% CI 0.39-0.64). When sensitivity was restricted to ≥90% for the 8- and 12-antigen panel, specificity was 2.2% (95% CI 0-17.7%) and 8.1% (95% CI 0-23.9%), respectively. A three-antigen combination (Rv0934-P38, Ag85A, and Rv2031-HSPX) outperformed both panels, with an AUC of 0.60 (95% CI 0.48-0.73), 90% sensitivity (95% CI 78.2-96.7%) and 29.7% specificity (95% CI 15.9-47%). The multi-antigen panels did not achieve the target accuracy for a TB triage test among PLHIV. We identified a new combination that improved performance for TB screening in an HIV-positive sample compared to an existing serological panel in Uganda, and suggests an approach to identify novel antigen combinations specifically for screening TB in PLHIV.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2018.2018 9 May 2019,. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/274453/9789241565646-eng....
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for intensified tuberculosis case-finding and isoniazid preventive therapy for people living with HIV in resource-constrained settings. 2011.
-
- Getahun H, Kittikraisak W, Heilig CM, Corbett EL, Ayles H, Cain KP, et al. Development of a standardized screening rule for tuberculosis in people living with HIV in resource-constrained settings: individual participant data meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS Med. 2011;8(1):e1000391 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000391 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

