Mutations in SREBF1, Encoding Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Transcription Factor 1, Cause Autosomal-Dominant IFAP Syndrome
- PMID: 32497488
- PMCID: PMC7332643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.05.006
Mutations in SREBF1, Encoding Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Transcription Factor 1, Cause Autosomal-Dominant IFAP Syndrome
Abstract
IFAP syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by ichthyosis follicularis, atrichia, and photophobia. Previous research found that mutations in MBTPS2, encoding site-2-protease (S2P), underlie X-linked IFAP syndrome. The present report describes the identification via whole-exome sequencing of three heterozygous mutations in SREBF1 in 11 unrelated, ethnically diverse individuals with autosomal-dominant IFAP syndrome. SREBF1 encodes sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1), which promotes the transcription of lipogenes involved in the biosynthesis of fatty acids and cholesterols. This process requires cleavage of SREBP1 by site-1-protease (S1P) and S2P and subsequent translocation into the nucleus where it binds to sterol regulatory elements (SRE). The three detected SREBF1 mutations caused substitution or deletion of residues 527, 528, and 530, which are crucial for S1P cleavage. In vitro investigation of SREBP1 variants demonstrated impaired S1P cleavage, which prohibited nuclear translocation of the transcriptionally active form of SREBP1. As a result, SREBP1 variants exhibited significantly lower transcriptional activity compared to the wild-type, as demonstrated via luciferase reporter assay. RNA sequencing of the scalp skin from IFAP-affected individuals revealed a dramatic reduction in transcript levels of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) and of keratin genes known to be expressed in the outer root sheath of hair follicles. An increased rate of in situ keratinocyte apoptosis, which might contribute to skin hyperkeratosis and hypotrichosis, was also detected in scalp samples from affected individuals. Together with previous research, the present findings suggest that SREBP signaling plays an essential role in epidermal differentiation, skin barrier formation, hair growth, and eye function.
Keywords: MBTPS2; SREBF1; atrichia; ichthyosis follicularis; photophobia; sterol biosynthesis.
Copyright © 2020 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
S.D.W. has served as a paid consultant to Allergan, Genentech, and Castle Biosciences; otherwise the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


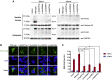


References
-
- McLeod J.M. Three cases of ‘ichthyosis follicularis’ associated with baldness. Br. J. Dermatol. 1909;21:165–189.
-
- Wang H.J., Tang Z.L., Lin Z.M., Dai L.L., Chen Q., Yang Y. Recurrent splice-site mutation in MBTPS2 underlying IFAP syndrome with Olmsted syndrome-like features in a Chinese patient. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2014;39:158–161. - PubMed
-
- Oeffner F., Fischer G., Happle R., König A., Betz R.C., Bornholdt D., Neidel U., Boente Mdel.C., Redler S., Romero-Gomez J. IFAP syndrome is caused by deficiency in MBTPS2, an intramembrane zinc metalloprotease essential for cholesterol homeostasis and ER stress response. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009;84:459–467. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ming A., Happle R., Grzeschik K.H., Fischer G. Ichthyosis follicularis, alopecia, and photophobia (IFAP) syndrome due to mutation of the gene MBTPS2 in a large Australian kindred. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2009;26:427–431. - PubMed
-
- Nakayama J., Iwasaki N., Shin K., Sato H., Kamo M., Ohyama M., Noguchi E., Arinami T. A Japanese case of ichthyosis follicularis with atrichia and photophobia syndrome with an MBTPS2 mutation. J. Hum. Genet. 2011;56:250–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

