Mucoadhesive Electrospun Fibre-Based Technologies for Oral Medicine
- PMID: 32498237
- PMCID: PMC7356016
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12060504
Mucoadhesive Electrospun Fibre-Based Technologies for Oral Medicine
Abstract
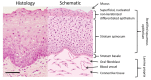
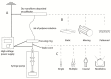
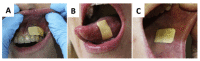
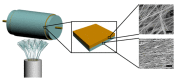
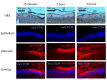
Oral disease greatly affects quality of life, as the mouth is required for a wide range of activities including speech, food and liquid consumption. Treatment of oral disease is greatly limited by the dose forms that are currently available, which suffer from short contact times, poor site specificity, and sensitivity to mechanical stimulation. Mucoadhesive devices prepared using electrospinning offer the potential to address these challenges by allowing unidirectional site-specific drug delivery through intimate contact with the mucosa and with high surface areas to facilitate drug release. This review will discuss the range of electrospun mucoadhesive devices that have recently been reported to address oral inflammatory diseases, pain relief, and infections, as well as new treatments that are likely to be enabled by this technology in the future.
Keywords: bioadhesion; drug delivery; electrospinning; infections; inflammation; local therapy; mucosa; oral cavity; pain relief.
Conflict of interest statement
Professor Paul V. Hatton is on the AFYX Therapeutics APS Scientific Advisory Board, where AFYX have translated mucoadhesive electrospun patch technology for clinical use and have intellectual property (international patent application WO 2017/085262. All authors have received funding from AFYX Therapeutics. The funders had no role in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

