Monitoring with In Vivo Electrochemical Sensors: Navigating the Complexities of Blood and Tissue Reactivity
- PMID: 32498360
- PMCID: PMC7308849
- DOI: 10.3390/s20113149
Monitoring with In Vivo Electrochemical Sensors: Navigating the Complexities of Blood and Tissue Reactivity
Abstract
The disruptive action of an acute or critical illness is frequently manifest through rapid biochemical changes that may require continuous monitoring. Within these changes, resides trend information of predictive value, including responsiveness to therapy. In contrast to physical variables, biochemical parameters monitored on a continuous basis are a largely untapped resource because of the lack of clinically usable monitoring systems. This is despite the huge testing repertoire opening up in recent years in relation to discrete biochemical measurements. Electrochemical sensors offer one of the few routes to obtaining continuous readout and, moreover, as implantable devices information referable to specific tissue locations. This review focuses on new biological insights that have been secured through in vivo electrochemical sensors. In addition, the challenges of operating in a reactive, biological, sample matrix are highlighted. Specific attention is given to the choreographed host rejection response, as evidenced in blood and tissue, and how this limits both sensor life time and reliability of operation. Examples will be based around ion, O2, glucose, and lactate sensors, because of the fundamental importance of this group to acute health care.
Keywords: O2; foreign body reaction; glucose; ion selective electrodes; lactate; metabolite sensors; sensor biocompatibility.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest, and neither sponsors nor any other party had a role into the materials collection or interpretation in this review.
Figures


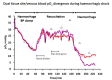

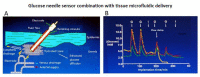
 ) venous blood glucose, tissue glucose at 60 µL/h microflow (
) venous blood glucose, tissue glucose at 60 µL/h microflow ( ) and at a constrained flow of 10 µL/h (
) and at a constrained flow of 10 µL/h ( ) showing underestimated glucose and total loss of response with clamped flow. Bolus tail vein administration of glucose (G) and insulin (I). Adapted from [83].
) showing underestimated glucose and total loss of response with clamped flow. Bolus tail vein administration of glucose (G) and insulin (I). Adapted from [83].References
-
- Land S.C., Porterfield D.M., Sanger R.H., Smith P.J.S. The self-referencing oxygen-selective microelectrode: Detection of transmembrane oxygen flux from single cells. J. Exp. Biol. 1999;202:211–218. - PubMed
-
- Wians E.H. Clinical Laboratory Tests: Which, Why, and What Do The Results Mean? Labmedicine. 2009;40:105–113. doi: 10.1309/LM404L0HHUTWWUDD. - DOI
-
- Rodenburg R.J.T., Schoonderwoerd G.C., Tiranti V., Taylor R.W., Rotig A., Valente L., Invernizzi F., Chretien D., He L., Backx G., et al. A multi-center comparison of diagnostic methods for the biochemical evaluation of suspected mitochondrial disorders. Mitochondrion. 2013;13:36–43. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2012.11.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

