Synthesis and Evaluation of a Thermoresponsive Degradable Chitosan-Grafted PNIPAAm Hydrogel as a "Smart" Gene Delivery System
- PMID: 32498464
- PMCID: PMC7321466
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13112530
Synthesis and Evaluation of a Thermoresponsive Degradable Chitosan-Grafted PNIPAAm Hydrogel as a "Smart" Gene Delivery System
Abstract
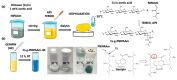
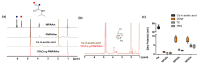
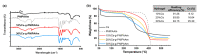
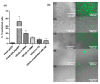
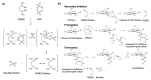
Thermoresponsive hydrogels demonstrate tremendous potential as sustained drug delivery systems. However, progress has been limited as formulation of a stable biodegradable thermosensitive hydrogel remains a significant challenge. In this study, free radical polymerization was exploited to formulate a biodegradable thermosensitive hydrogel characterized by sustained drug release. Highly deacetylated chitosan and N-isopropylacrylamide with distinctive physical properties were employed to achieve a stable, hydrogel network at body temperature. The percentage of chitosan was altered within the copolymer formulations and the subsequent physical properties were characterized using 1H-NMR, FTIR, and TGA. Viscoelastic, swelling, and degradation properties were also interrogated. The thermoresponsive hydrogels were loaded with RALA/pEGFP-N1 nanoparticles and release was examined. There was sustained release of nanoparticles over three weeks and, more importantly, the nucleic acid cargo remained functional and this was confirmed by successful transfection of the NCTC-929 fibroblast cell line. This tailored thermoresponsive hydrogel offers an option for sustained delivery of macromolecules over a prolonged considerable period.
Keywords: drug delivery; hydrogel; hydroxyapatite; nanoparticles; thermoresponsive.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Injectable Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Formed by Alginate-g-Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) That Releases Doxorubicin-Encapsulated Micelles as a Smart Drug Delivery System.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Oct 18;9(41):35673-35682. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b12849. Epub 2017 Oct 2. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 28937214
-
Injectable Depot Forming Thermoresponsive Hydrogel for Sustained Intrascleral Delivery of Sunitinib Using Hollow Microneedles.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Jul-Aug;38(6):433-448. doi: 10.1089/jop.2022.0016. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35914241
-
Smart composite materials based on chitosan microspheres embedded in thermosensitive hydrogel for controlled delivery of drugs.Carbohydr Polym. 2017 Feb 10;157:493-502. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.022. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Carbohydr Polym. 2017. PMID: 27987954
-
Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm) based thermosensitive injectable hydrogels for biomedical applications.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014 Nov;88(3):575-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.07.005. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014. PMID: 25092423 Review.
-
Thermosensitive polymeric hydrogels as drug delivery systems.Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(1):79-94. Curr Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23092130 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrogel Based on Nanoclay and Gelatin Methacrylate Polymeric Matrix as a Potential Osteogenic Application.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Jan 29;14(2):74. doi: 10.3390/jfb14020074. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36826873 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature-Responsive Injectable Composite Hydrogels Based on Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide), Chitosan, and Hemp-Derived Cellulose Nanocrystals.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Oct 24;16(21):2984. doi: 10.3390/polym16212984. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518194 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Ellipsoid Chitosan-Phthalate Lecithin Nanoparticles for siRNA Delivery.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Jul 28;9:695371. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.695371. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34395401 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Review of the State-of-the-Art.Gels. 2022 Jul 20;8(7):454. doi: 10.3390/gels8070454. Gels. 2022. PMID: 35877539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan: A Potential Biopolymer in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 21;15(4):1313. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041313. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111795 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoare T.R., Kohane D.S. Hydrogels in drug delivery: Progress and challenges. Polymer. 2008;49:1993–2007. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2008.01.027. - DOI
-
- Caló E., Khutoryanskiy V.V. Biomedical applications of hydrogels: A review of patents and commercial products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015;65:252–267. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2014.11.024. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

