Cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking for characterization of patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: correlation of global longitudinal strain with invasive diastolic functional indices
- PMID: 32498688
- PMCID: PMC7271439
- DOI: 10.1186/s12968-020-00636-w
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking for characterization of patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: correlation of global longitudinal strain with invasive diastolic functional indices
Abstract
Background: Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction is the main cause of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), and is characterized by LV stiffness and relaxation. Abnormal LV global longitudinal strain (GLS) is frequently observed l in HFpEF, and was shown to be useful in identifying HFpEF patients at high risk for a cardiovascular event. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) feature tracking (CMR-FT) enables the reproducible and non-invasive assessment of global strain from cine CMR images. However, the association between GLS and invasively measured parameters of diastolic function has not been investigated. We sought to determine the prevalence and severity of GLS impairment in patients with HFpEF by using CMR-FT, and to evaluate the correlation between GLS measured by CMR-FT and that measured by invasive diastolic functional indices.
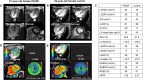
Methods: Eighteen patients with HFpEF and 18 age- and sex-matched healthy control subjects were studied. All subjects underwent cine, pre- and post-contrast T1 mapping and late gadolinium-enhancement CMR. In the HFpEF patients, invasive pressure-volume loops were obtained to evaluate LV diastolic properties. GLS was quantified from cine CMR, and extracellular volume fraction (ECV) was quantified from pre- and post-contrast T1 mapping as a known imaging biomarker for predicting LV stiffness.
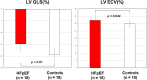
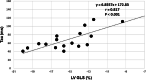
Results: GLS was significantly impaired in patients with HFpEF (- 14.8 ± 3.3 vs.-19.5 ± 2.8%, p < 0.001). Thirty nine percent (7/18) of HFpEF patients showed impaired GLS with a cut-off of - 13.9%. Statistically significant difference was found in ECV between HFpEF patients and controls (32.2 ± 3.8% vs. 29.9 ± 2.6%, p = 0.044). In HFpEF patients, the time constant of active LV relaxation (Tau) was strongly correlated with GLS (r = 0.817, p < 0.001), global circumferential strain (GCS) (r = 0.539, p = 0.021) and global radial strain (GRS) (r = - 0.552, p = 0.017). Multiple linear regression analysis revealed GLS as the only independent predictor of altered Tau (beta = 0.817, p < 0.001) among age, LV end-diastolic volume index, LV end-systolic volume index, LV mass index, GCS, GRS and GLS.
Conclusions: CMR-FT is a noninvasive approach that enables identification of the subgroup of HFpEF patients with impaired GLS. CMR LV GLS independently predicts abnormal invasive LV relaxation index Tau measurements in HFpEF patients. These findings suggest that feature-tracking CMR analysis in conjunction with ECV, may enable evaluation of diastolic dysfunction in patients with HFpEF.
Keywords: Cardiovascular magnetic resonance; Extracellular volume fraction; Feature tracking; Global longitudinal strain; Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Conflict of interest statement
Hajime Sakuma, MD receives departmental research grant support from Daiichi Sankyo Company Limited, FUJIFILM Holdings Corporation, Nihon Medi-Physics Co., Ltd
Figures

Similar articles
-
Layer-specific strain in patients with heart failure using cardiovascular magnetic resonance: not all layers are the same.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2020 Dec 3;22(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12968-020-00680-6. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2020. PMID: 33267877 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Volume Fraction for Characterization of Patients With Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Apr 19;67(15):1815-1825. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.02.018. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27081022 Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of Left Atrial Function on Exercise Capacity and Left Ventricular Function in Patients With Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017 Apr;10(4):e005467. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.116.005467. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28360259
-
Myocardial Strain Measurements Derived From MR Feature-Tracking: Influence of Sex, Age, Field Strength, and Vendor.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024 Apr;17(4):364-379. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2023.05.019. Epub 2023 Jul 19. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37480906
-
Left Atrial Strain in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Narrative Review.Life (Basel). 2025 Feb 17;15(2):313. doi: 10.3390/life15020313. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diastolic Cardiac Function by MRI-Imaging Capabilities and Clinical Applications.Tomography. 2021 Dec 8;7(4):893-914. doi: 10.3390/tomography7040075. Tomography. 2021. PMID: 34941647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Cardiovascular Diagnostics: The Expanding Role of CMR in Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathies.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 28;14(3):865. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030865. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-time cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging for non-invasive characterisation of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: final outcomes of the HFpEF stress trial.Clin Res Cardiol. 2024 Mar;113(3):496-508. doi: 10.1007/s00392-023-02363-5. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Clin Res Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38170248 Free PMC article.
-
Blunted cardiovascular effects of beta-blockers in patients with cirrhosis: Relation to severity?PLoS One. 2022 Jun 28;17(6):e0270603. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270603. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35763518 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in Aging-related Myocardial Stiffening Quantitatively Measured with MR Elastography.Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2024 Jun;6(3):e230140. doi: 10.1148/ryct.230140. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38780427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinberg BA, Zhao X, Heidenreich PA, Peterson ED, Bhatt DL, Cannon CP, et al. Get with the guidelines scientific advisory committee and investigators. Trends in patients hospitalized with heart failure and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction: prevalence, therapies, and outcomes. Circulation. 2012;126:65–75. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.080770. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

