U-shaped association between plasma sphingosine-1-phosphate levels and mortality in patients with chronic systolic heart failure: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 32498720
- PMCID: PMC7273664
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-020-01262-2
U-shaped association between plasma sphingosine-1-phosphate levels and mortality in patients with chronic systolic heart failure: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: The endogenous lipid molecule sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) has received attention in the cardiovascular field due to its significant cardioprotective effects, as revealed in animal studies. The purpose of our study was to identify the distribution characteristics of S1P in systolic heart failure patients and the prognostic value of S1P for long-term prognosis.
Methods: We recruited 210 chronic systolic heart failure patients from June 2014 to December 2015. Meanwhile 54 healthy people in the same area were selected as controls. Plasma S1P was measured by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Patients were grouped according to the baseline S1P level quartiles, and restricted cubic spline plots described the association between S1P and all-cause death. Cox proportional hazard analysis was used to determine the relationship between category of S1P and all-cause death.
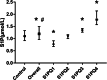
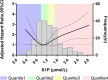
Results: Compared with the control group, the plasma S1P in chronic heart failure patients demonstrated a higher mean level (1.269 μmol/L vs 1.122 μmol/L, P = 0.006) and a larger standard deviation (0.441 vs 0.316, P = 0.022). Based on multivariable Cox regression with restricted cubic spline analysis, a non-linear and U-shaped association between S1P levels and the risk of all-cause death was observed. After a follow-up period of 31.7 ± 10.3 months, the second quartile (0.967-1.192 μml/L) with largely normal S1P levels had the lowest all-cause mortality and either an increase (adjusted HR = 2.368, 95%CI 1.006-5.572, P = 0.048) or a decrease (adjusted HR = 0.041, 95%CI 0.002-0.808, P = 0.036) predicted a worse prognosis. The survival curves showed that patients in the lowest quartile and highest quartile were at a higher risk of death.
Conclusions: Plasma S1P levels in systolic heart failure patients are related to the long-term all-cause mortality with a U-shaped correlation.
Trial registration: CHiCTR, ChiCTR-ONC-14004463. Registered 20 March 2014.
Keywords: All-cause mortality; Heart failure; Prognosis; Sphingosine-1-phosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plasma sphingosine-1-phosphate concentrations are associated with systolic heart failure in patients with ischemic heart disease.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 Sep;110:35-37. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28709768
-
Low sphingosine-1-phosphate plasma levels are predictive for increased mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 23;12(3):e0174424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174424. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28334008 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Levels Are Associated With Severity and Outcome in Patients With Cerebral Ischemia.Stroke. 2021 Dec;52(12):3901-3907. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.033414. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 34496616
-
Novel Insights into the Role of HDL-Associated Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Cardiometabolic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 12;20(24):6273. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246273. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31842389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
U-Shaped Relationship of Sodium-to-chloride Ratio on admission and Mortality in Elderly Patients with Heart Failure: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023 Jan;48(1):101419. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101419. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36181785 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of sphingolipids in heart failure.Eur Heart J Open. 2025 May 2;5(3):oeaf035. doi: 10.1093/ehjopen/oeaf035. eCollection 2025 May. Eur Heart J Open. 2025. PMID: 40322641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipid Metabolism and Signalling Pathways in Heart Failure: From Molecular Mechanism to Therapeutic Potential.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Apr 23;18:5477-5498. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S515757. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40291458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate and its regulatory role in vascular endothelial cells.Histol Histopathol. 2022 Mar;37(3):213-225. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-428. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Histol Histopathol. 2022. PMID: 35118637 Review.
-
Deficiency of the sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) transporter Mfsd2b protects the heart against hypertension-induced cardiac remodeling by suppressing the L-type-Ca2+ channel.Basic Res Cardiol. 2024 Oct;119(5):853-868. doi: 10.1007/s00395-024-01073-x. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Basic Res Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39110173 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Derived Lipid and Metabolite Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Research from Clinical Studies: A Recent Update.Cells. 2023 Dec 8;12(24):2796. doi: 10.3390/cells12242796. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132115 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, et al. 2016 esc guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the european society of cardiology (esc). Developed with the special contribution of the heart failure association (hfa) of the esc. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(27):2129–2200. - PubMed
-
- Ej B, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56–e528. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

