DPD Quantification in Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Novel Imaging Biomarker
- PMID: 32498921
- PMCID: PMC7264710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.03.020
DPD Quantification in Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Novel Imaging Biomarker
Erratum in
-
Correction.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021 Jan;14(1):318-319. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.12.001. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33413886 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objectives: To assess whether single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT/CT) quantification of bone scintigraphy would improve diagnostic accuracy and offer a means of quantifying amyloid burden.
Background: Transthyretin-related cardiac amyloidosis is common and can be diagnosed noninvasively using bone scintigraphy; interpretation, however, relies on planar images. SPECT/CT imaging offers 3-dimensional visualization.
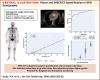
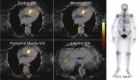
Methods: This was a single-center, retrospective analysis of 99mTc-3,3-diphosphono-1,2-propanodicarboxylic acid (DPD) scans reported using the Perugini grading system (0 = negative; 1 to 3 = increasingly positive). Conventional planar quantification techniques (heart/contralateral lung, and heart/whole-body retention ratios) were performed. Heart, adjacent vertebra, paraspinal muscle and liver peak standardized uptake values (SUVpeak) were recorded from SPECT/CT acquisitions. An SUV retention index was also calculated: (cardiac SUVpeak/vertebral SUVpeak) × paraspinal muscle SUVpeak. In a subgroup of patients, SPECT/CT quantification was compared with myocardial extracellular volume quantification by CT imaging (ECVCT).
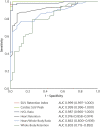
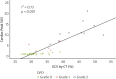
Results: A total of 100 DPD scans were analyzed (patient age 84 ± 9 years; 52% male): 40 were Perugini grade 0, 12 were grade 1, 41 were grade 2, and 7 were grade 3. Cardiac SUVpeak increased from grade 0 to grade 2; however, it plateaued between grades 2 and 3 (p < 0.001). Paraspinal muscle SUVpeak increased with grade (p < 0.001), whereas vertebral SUVpeak decreased (p < 0.001). The composite parameter of SUV retention index overcame the plateauing of the cardiac SUVpeak and increased across all grades (p < 0.001). Cardiac SUVpeak correlated well (r2 = 0.73; p < 0.001) with ECVCT. Both the cardiac SUVpeak and SUV retention index had excellent diagnostic accuracy (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.999). The heart to contralateral lung ratio performed the best of the planar quantification techniques (AUC: 0.987).
Conclusions: SPECT/CT quantification in DPD scintigraphy is possible and outperforms planar quantification techniques. Differentiation of Perugini grade 2 or 3 is confounded by soft tissue uptake, which can be overcome by a composite SUV retention index. This index can help in the diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis and may offer a means of monitoring response to therapy.
Keywords: DPD scintigraphy; SPECT/CT quantification; cardiac amyloidosis.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Quantitative Bone-Avid Tracer SPECT/CT for Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Crucial Step Forward.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Jun;13(6):1364-1367. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.05.005. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32498922 No abstract available.
References
-
- González-López E., Gallego-Delgado M., Guzzo-Merello G. Wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis as a cause of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:2585–2594. - PubMed
-
- Gillmore J.D., Maurer M.S., Falk R.H. Nonbiopsy diagnosis of cardiac transthyretin amyloidosis. Circulation. 2016;133:2404–2412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

