SIRT1 accelerates the progression of activity-based anorexia
- PMID: 32499508
- PMCID: PMC7272424
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16348-9
SIRT1 accelerates the progression of activity-based anorexia
Abstract
Food consumption is fundamental for life, and eating disorders often result in devastating or life-threatening conditions. Anorexia nervosa (AN) is characterized by a persistent restriction of energy intake, leading to lowered body weight, constant fear of gaining weight, and psychological disturbances of body perception. Herein, we demonstrate that SIRT1 inhibition, both genetically and pharmacologically, delays the onset and progression of AN behaviors in activity-based anorexia (ABA) models, while SIRT1 activation accelerates ABA phenotypes. Mechanistically, we suggest that SIRT1 promotes progression of ABA, in part through its interaction with NRF1, leading to suppression of a NMDA receptor subunit Grin2A. Our results suggest that AN may arise from pathological positive feedback loops: voluntary food restriction activates SIRT1, promoting anxiety, hyperactivity, and addiction to starvation, exacerbating the dieting and exercising, thus further activating SIRT1. We propose SIRT1 inhibition can break this cycle and provide a potential therapy for individuals suffering from AN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
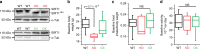

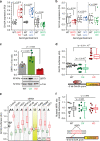
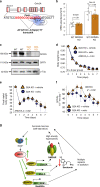
References
-
- Treasure J, et al. Anorexia nervosa. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015;1:15074. - PubMed
-
- Davis C. Excessive exercise and anorexia nervosa: addictive and compulsive behaviors. Psychiat Ann. 1999;29:221–224.
-
- McNulty PA. Prevalence and contributing factors of eating disorder behaviors in active duty service women in the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marines. Mil. Med. 2001;166:53–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

