Patient-controlled subcutaneous analgesia using sufentainil or morphine in home care treatment in patients with stage III-IV cancer: A multi-center randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 32500675
- PMCID: PMC7402833
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3194
Patient-controlled subcutaneous analgesia using sufentainil or morphine in home care treatment in patients with stage III-IV cancer: A multi-center randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Purpose: Patient-controlled subcutaneous analgesia (PCSA) with sufentanil is an alternative analgesia strategy in patients with stage III-IV cancer; however, its efficacy and safety have not been fully investigated.
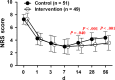
Methods: From May 10, 2017 to November 10, 2017, 120 patients with stage III-IV cancer suffering from moderate to severe pain were prospectively enrolled from six hospitals and randomized to receive PCSA with morphine (control group) or sufentanil (intervention group). Before the PCSA and on days 1, 3, 7, 14, 28, and 56 after treatment, the numeric rating scale (NRS) and 36-item Short Form health survey (SF-36) were completed for each patient and the side effects were also recorded.
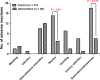
Results: No significant differences (P > .05) were observed in the preoperative NRS score and the SF-36 parameters between the two groups. Patients in the intervention group achieved better pain relief, as indicated by lower NRS scores at days 14 (P = .040), 28 (P < .001), and 56 (P < .001) after PCSA device implantation (vs control group). Furthermore, the patients in the intervention group also achieved a better life quality, as indicated by the physical role, general health, social function body pain, and mental health scores. Finally, the patients receiving sufentanil showed lower levels of nausea and somnolence than those in the control group.
Conclusion: PCSA with sufentanil achieves better pain control and life quality as well as fewer adverse reactions in stage III-IV cancer patients with pain and may be a promising pain management in these patients.
Trial registration: This study was registered at chictr.org.cn with the trial number: ChiCTR-IPR-17011280.
Keywords: 36-item Short Form health survey; advanced cancer; numeric rating scale; patient-controlled subcutaneous analgesia; sufentanil.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prospective investigation of intravenous patient-controlled analgesia with hydromorphone or sufentanil: impact on mood, opioid adverse effects, and recovery.BMC Anesthesiol. 2018 Apr 10;18(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0500-1. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 29636011 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Patient Controlled Subcutaneous Analgesia of Hydromorphone Versus Morphine to Treat Moderate and Severe Cancer Pain: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial.J Pain Symptom Manage. 2024 Jan;67(1):50-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2023.09.018. Epub 2023 Sep 23. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2024. PMID: 37742793 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative efficacy of patient-controlled administration of morphine, hydromorphone, or sufentanil for the treatment of oral mucositis pain following bone marrow transplantation.Pain. 1997 Sep;72(3):333-46. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(97)00059-6. Pain. 1997. PMID: 9313274 Clinical Trial.
-
A review of sufentanil and the sufentanil sublingual tablet system for acute moderate to severe pain.Pain Manag. 2015;5(4):237-50. doi: 10.2217/pmt.15.22. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Pain Manag. 2015. PMID: 26088280 Review.
-
Sufentanil versus fentanyl for pain relief in labor involving combined spinal-epidural analgesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;76(4):501-506. doi: 10.1007/s00228-019-02806-x. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31912188
Cited by
-
Patient-Controlled Subcutaneous Analgesia with Hydromorphone versus Oral Oxycontin for Opioid Titration of Cancer Pain: A Prospective Multicenter Randomized Trial.J Pain Res. 2024 Apr 12;17:1441-1451. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S451698. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38628430 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the efficacy of Sufentanil and Morphine Titration for patient-controlled Subcutaneous Analgesia in severe advanced cancer pain.Pak J Med Sci. 2023 Mar-Apr;39(2):561-566. doi: 10.12669/pjms.39.2.6664. Pak J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36950428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Connor AB, Turk DC, Dworkin RH, et al. Abuse liability measures for use in analgesic clinical trials in patients with pain: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2013;154:2324‐2334. - PubMed
-
- Turk DC, Dworkin RH, Allen RR, et al. Core outcome domains for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain. 2003;106:337‐345. - PubMed
-
- Lux EA, Heine, J . [Home care treatment of cancer pain patients with patient‐controlled analgesia (PCA)]. Schmerz. 2011;25:663‐667. - PubMed
-
- Schiessl C, Bidmon J, Sittl R, et al. Patient‐controlled analgesia (PCA) in outpatients with cancer pain. Analysis of 1,692 treatment days. Schmerz. 2007;21(35–8):40‐42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

