Neutral DNA-avidin nanoparticles as ultrasensitive reporters in immuno-PCR
- PMID: 32500871
- PMCID: PMC7412439
- DOI: 10.1039/d0an00134a
Neutral DNA-avidin nanoparticles as ultrasensitive reporters in immuno-PCR
Abstract
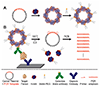
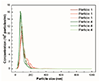
We have developed an immuno-PCR based diagnostic platform which couples detection antibodies to self-assembled, ultra-detectable DNA-avidin nanoparticles stabilized with poly(ethylene glycol) to link DNA amplification to target protein concentration. Electrostatic neutralization and cloaking of the PCR-amplifiable DNA labels by avidin and PEG coating reduces non-specific "stickiness" and enhances assay sensitivity. We further optimized the detectability of the nanoparticles by incorporating four repeats of a unique synthetic DNA PCR target into each nanoparticle. Using human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (hCG) as a model analyte, this platform was able to quantitate the target hCG protein in femtomolar concentrations using only standard laboratory equipment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

