Forecast and evaluation of COVID-19 spreading in USA with reduced-space Gaussian process regression
- PMID: 32501372
- PMCID: PMC7242925
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109924
Forecast and evaluation of COVID-19 spreading in USA with reduced-space Gaussian process regression
Abstract
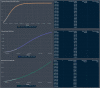
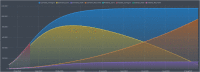
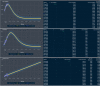
In this report, we analyze historical and forecast infections for COVID-19 death based on Reduced-Space Gaussian Process Regression associated to chaotic Dynamical Systems with information obtained in 82 days with continuous learning, day by day, from January 21 th , 2020 to April 12 th . According last results, COVID-19 could be predicted with Gaussian models mean-field models can be meaning- fully used to gather a quantitative picture of the epidemic spreading, with infections, fatality and recovery rate. The forecast places the peak in USA around July 14 th 2020, with a peak number of 132,074 death with infected individuals of about 1,157,796 and a number of deaths at the end of the epidemics of about 132,800. Late on January, USA confirmed the first patient with COVID-19, who had recently traveled to China, however, an evaluation of states in USA have demonstrated a fatality rate in China (4%) is lower than New York (4.56%), but lower than Michigan (5.69%). Mean estimates and uncertainty bounds for both USA and his cities and other provinces have increased in the last three months, with focus on New York, New Jersey, Michigan, California, Massachusetts, ... (January e April 12 th ). Besides, we propose a Reduced-Space Gaussian Process Regression model predicts that the epidemic will reach saturation in USA on July 2020. Our findings suggest, new quarantine actions with more restrictions for containment strategies implemented in USA could be successfully, but in a late period, it could generate critical rate infections and death for the next 2 month.
Keywords: COVID-19; Forecast; Gaussian; USA.
© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures
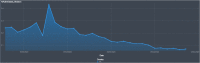
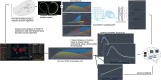
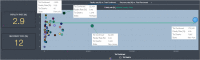
References
-
- Neher R.A., Dyrdak R., Druelle V., Hodcroft E.B., Albert J. Potential impact of seasonal forcing on a SARS-cov-2 pandemic. medRxiv. 2020 - PubMed
-
Published online March 3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

