Pathogenic Leptospira species in rodents from Corsica (France)
- PMID: 32502160
- PMCID: PMC7274395
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233776
Pathogenic Leptospira species in rodents from Corsica (France)
Abstract
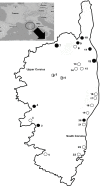
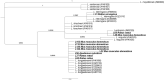
Leptospirosis is a worldwide emerging zoonotic disease caused by Leptospira species, that in some patients develop severe forms with high mortality. In France, Corsica is the area where the highest incidences have been reported. The present study was focused on the analysis of pathogenic Leptospira species in rodents of Corsica, as these micromammals are the main natural reservoirs of the bacteria, in order to identify the circulating species and to locate possible risk focuses of transmission, as no previous study on the presence of Leptospira species has been carried out in the island. Rattus rattus, Rattus norvegicus, Apodemus sylvaticus and Mus musculus domesticus were captured in the proximity of water sources along Corsica, the detection of pathogenic Leptospira species was carried out by amplification of the LipL32 gene. The bacteria were found in all the rodent species analyzed and widely. The general prevalence was 10.4%, reaching the maximum value in Bastia (45%). Leptospira interrogans and Leptospira borgpetersenii were identified by phylogenetic analysis, but also two sequences which corresponded to an unnamed Leptospira species, only previously found in rodents of New Caledonia. The high incidence of human leptospirosis in Corsica could be partially explained by the wide distribution of pathogenic Leptospira species identified in this study. Also, the presence of an unknown pathogenic species of Leptospira in an area with high prevalence, may be involved in the higher incidence of Leptospirosis in this island, however, the zoonotic capacity of this species remains unknown. The results obtained are interesting for public health since all positive samples were found near water sources and one of the routes of transmission of leptospirosis is contact with contaminated water. This information could help the competent entities to take preventive measures, reducing the incidence of human leptospirosis in Corsica.
Conflict of interest statement
“The authors have declared that no competing interests exist."
Figures
References
-
- Centre National de Référence de la Leptospirose. Rapport annuel d’activité Année d’exercice 2017. Paris: Institut Pasteur; 2018;38.

