Extracorporeal CO2 Removal and the Alveolar Gas Equation
- PMID: 32502357
- PMCID: PMC7528807
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202005-1609LE
Extracorporeal CO2 Removal and the Alveolar Gas Equation
Figures
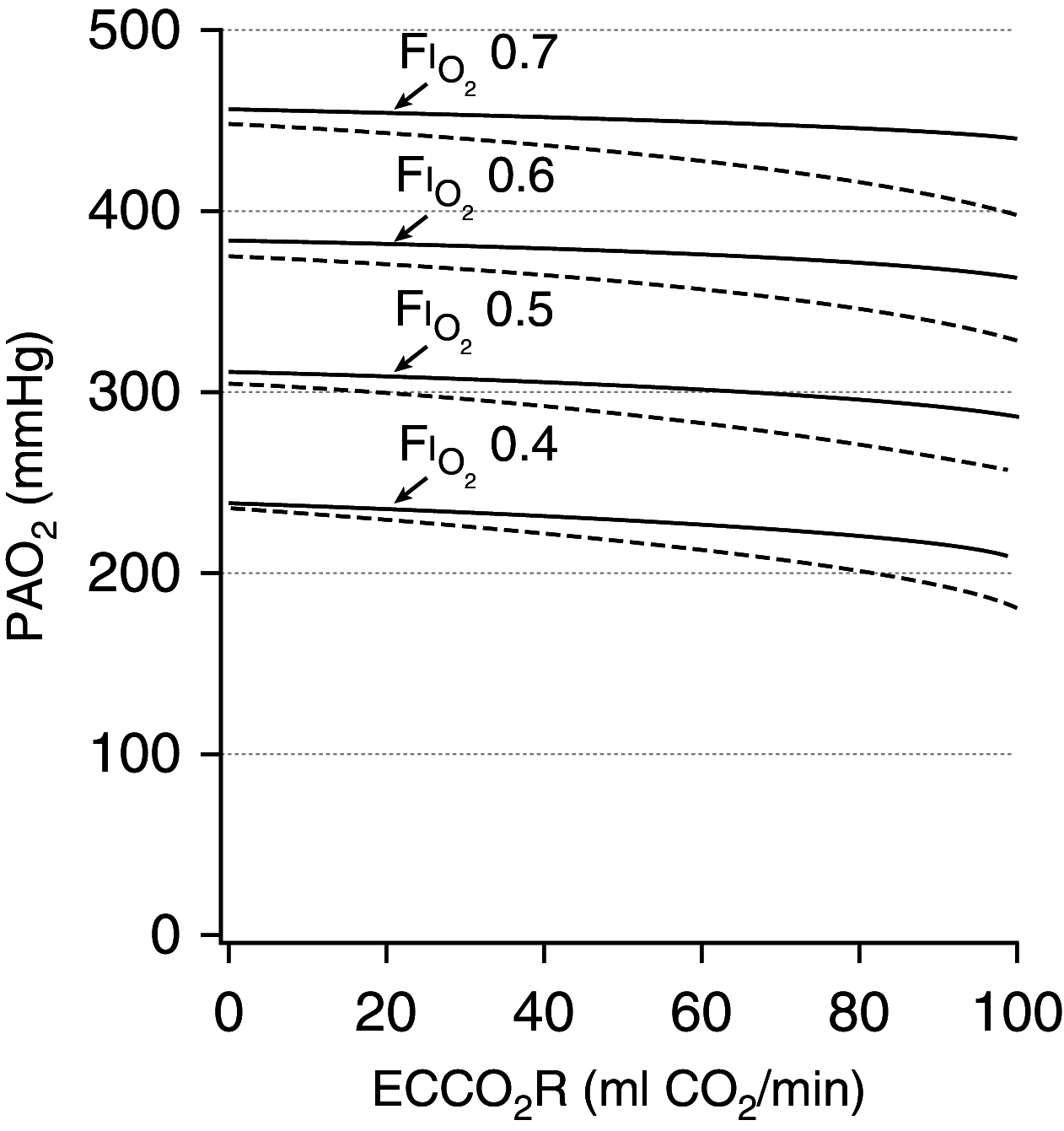
Comment in
-
Reply to Dickstein: Extracorporeal CO2 Removal and the Alveolar Gas Equation.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Oct 1;202(7):1058-1059. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202005-1923LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32502355 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Mechanical Ventilation for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome during Extracorporeal Life Support. Research and Practice.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Mar 1;201(5):514-525. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201907-1283CI. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 31726013 Review.
References
-
- Abrams D, Schmidt M, Pham T, Beitler JR, Fan E, Goligher EC, et al. Mechanical ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome during extracorporeal life support: research and practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201:514–525. - PubMed
-
- West JB. Respiratory physiology: the essentials. 6th ed. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

