Supervised Learning Occurs in Visual Perceptual Learning of Complex Natural Images
- PMID: 32502415
- PMCID: PMC7415644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.05.050
Supervised Learning Occurs in Visual Perceptual Learning of Complex Natural Images
Abstract
There have been long-standing debates regarding whether supervised or unsupervised learning mechanisms are involved in visual perceptual learning (VPL) [1-14]. However, these debates have been based on the effects of simple feedback only about response accuracy in detection or discrimination tasks of low-level visual features such as orientation [15-22]. Here, we examined whether the content of response feedback plays a critical role for the acquisition and long-term retention of VPL of complex natural images. We trained three groups of human subjects (n = 72 in total) to better detect "grouped microcalcifications" or "architectural distortion" lesions (referred to as calcification and distortion in the following) in mammograms either with no trial-by-trial feedback, partial trial-by-trial feedback (response correctness only), or detailed trial-by-trial feedback (response correctness and target location). Distortion lesions consist of more complex visual structures than calcification lesions [23-26]. We found that partial feedback is necessary for VPL of calcifications, whereas detailed feedback is required for VPL of distortions. Furthermore, detailed feedback during training is necessary for VPL of distortion and calcification lesions to be retained for 6 months. These results show that although supervised learning is heavily involved in VPL of complex natural images, the extent of supervision for VPL varies across different types of complex natural images. Such differential requirements for VPL to improve the detectability of lesions in mammograms are potentially informative for the professional training of radiologists.
Keywords: breast cancer; feedback; high-level vision; mammogram; natural stimuli; radiology; supervised learning; unsupervised learning; visual perceptual learning.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
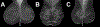

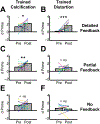
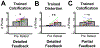
Comment in
-
Perceptual Expertise: How Is It Achieved?Curr Biol. 2020 Aug 3;30(15):R875-R878. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.06.013. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32750346
Similar articles
-
Deep Neural Networks for Modeling Visual Perceptual Learning.J Neurosci. 2018 Jul 4;38(27):6028-6044. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1620-17.2018. Epub 2018 May 23. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29793979 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Strategy Video Game Experience and Visual Perceptual Learning.J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 22;35(29):10485-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3340-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26203143 Free PMC article.
-
Category-Induced Transfer of Visual Perceptual Learning.Curr Biol. 2019 Apr 22;29(8):1374-1378.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 30930042 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptual learning: toward a comprehensive theory.Annu Rev Psychol. 2015 Jan 3;66:197-221. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010814-015214. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Annu Rev Psychol. 2015. PMID: 25251494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-stage model in perceptual learning: toward a unified theory.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014 May;1316:18-28. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12419. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014. PMID: 24758723 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A hole in a piece of cardboard and predictive brain: the incomprehension of modern art in the light of the predictive coding paradigm.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Jan 29;379(1895):20220417. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0417. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38104613 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptual learning improves discrimination but does not reduce distortions in appearance.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 Apr 15;21(4):e1012980. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012980. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40233123 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning approach identified clusters for patients with low cardiac output syndrome and outcomes after cardiac surgery.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 18;9:962992. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.962992. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36061544 Free PMC article.
-
What do radiologists look for? Advances and limitations of perceptual learning in radiologic search.J Vis. 2020 Oct 1;20(10):17. doi: 10.1167/jov.20.10.17. J Vis. 2020. PMID: 33057623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anterograde interference in multitask perceptual learning.NPJ Sci Learn. 2025 May 9;10(1):23. doi: 10.1038/s41539-025-00312-7. NPJ Sci Learn. 2025. PMID: 40346059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poggio T, Fahle M, and Edelman S (1992). Fast perceptual learning in visual hyperacuity. Science 256, 1018–1021. - PubMed
-
- Weiss Y, Edelman S, and Fahle M (1993). Models of perceptual learning in vernier hyperacuity. Neural Computation 5, 695–718.
-
- Sundareswaran V, and Vaina LM (1996). Adaptive computational models of fast learning of motion direction discrimination. Biological Cybernetics 74, 319–329. - PubMed
-
- Herzog MH, and Fahle M (1998). Modeling perceptual learning: difficulties and how they can be overcome. Biological Cybernetics 78, 107–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

