PunctaSpecks: A tool for automated detection, tracking, and analysis of multiple types of fluorescently labeled biomolecules
- PMID: 32502904
- PMCID: PMC7343294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102224
PunctaSpecks: A tool for automated detection, tracking, and analysis of multiple types of fluorescently labeled biomolecules
Abstract
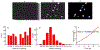
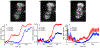
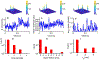
Recent advances in imaging technology and fluorescent probes have made it possible to gain information about the dynamics of subcellular processes at unprecedented spatiotemporal scales. Unfortunately, a lack of automated tools to efficiently process the resulting imaging data encoding fine details of the biological processes remains a major bottleneck in utilizing the full potential of these powerful experimental techniques. Here we present a computational tool, called PunctaSpecks, that can characterize fluorescence signals arising from a wide range of biological molecules under normal and pathological conditions. Among other things, the program can calculate the number, areas, life-times, and amplitudes of fluorescence signals arising from multiple sources, track diffusing fluorescence sources like moving mitochondria, and determine the overlap probability of two processes or organelles imaged using indicator dyes of different colors. We have tested PunctaSpecks on synthetic time-lapse movies containing mobile fluorescence objects of various sizes, mimicking the activity of biomolecules. The robustness of the software is tested by varying the level of noise along with random but known pattern of appearing, disappearing, and movement of these objects. Next, we use PunctaSpecks to characterize protein-protein interaction involved in store-operated Ca2+ entry through the formation and activation of plasma membrane-bound ORAI1 channel and endoplasmic reticulum membrane-bound stromal interaction molecule (STIM), the evolution of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3)-induced Ca2+ signals from sub-micrometer size local events into global waves in human cortical neurons, and the activity of Alzheimer's disease-associated β amyloid pores in the plasma membrane. The tool can also be used to study other dynamical processes imaged through fluorescence molecules. The open source algorithm allows for extending the program to analyze more than two types of biomolecules visualized using markers of different colors.
Keywords: Amyloid beta pores; Characterizing fluorescence data; Human cortical neurons; ORAI1-STIM1 interaction; PunctaSpecks; Tracking fluorescence molecules.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




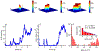
References
-
- Alvarez LAJ, Widzgowski B, Ossato G, van den Broek B, Jalink K, Kuschel L, Roberti MJ, Hecht F, SP8 FALCON: a novel concept in fluorescence lifetime imaging enabling video-rate confocal FLIM, Nat Methods, 16 (2019).
-
- Tsien RY, Imagining imaging’s future, Nat Cell Biol, (2003) Ss16–Ss21. - PubMed
-
- Stephens DJ, Allan VJ, Light microscopy techniques for live cell Imaging, Science, 300 (2003) 82–86. - PubMed
-
- Lippincott-Schwartz J, Patterson GH, Development and use of fluorescent protein markers in living cells, Science, 300 (2003) 87–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

