Construction of Antibody Phage Libraries and Their Application in Veterinary Immunovirology
- PMID: 32503103
- PMCID: PMC7345743
- DOI: 10.3390/antib9020021
Construction of Antibody Phage Libraries and Their Application in Veterinary Immunovirology
Abstract
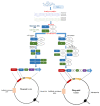
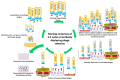
Antibody phage display (APD) technology has revolutionized the field of immunovirology with its application in viral disease diagnostics and antiviral therapy. This robust and versatile technology allows the expression of an antibody fused to a phage coat protein on the surface of a filamentous phage. The DNA sequence coding for the antibody is packaged within the phage, linking the phenotype to genotype. Antibody phage display inherits the ability to rapidly generate and modify or improve high-affinity monoclonal antibodies, rendering it indispensable in immunology. In the last two decades, phage-display-derived antibodies have been extensively used in human medicine as diagnostic and therapeutic modalities. Recently, they are also gaining significant ground in veterinary medicine. Even though these advancements are mainly biased towards economically important animals such as chicken, cattle, and pigs, they are laying the foundation of fulfilling the unmet needs of veterinary medicine as antibody-based biologics in viral diagnostics, therapeutics, and immunoprophylaxis. This review provides a brief overview of the construction of antibody phage libraries and their application in diagnosis, prevention, and control of infectious viral diseases in veterinary medicine in detail.
Keywords: immunovirology; monoclonal antibody; phage display; veterinary medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

