A 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid-Gelatin Conjugate Inhibits the Basal and Hsp90-Stimulated Migration and Invasion of Tumor Cells
- PMID: 32503118
- PMCID: PMC7353502
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb11020039
A 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid-Gelatin Conjugate Inhibits the Basal and Hsp90-Stimulated Migration and Invasion of Tumor Cells
Abstract
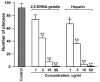
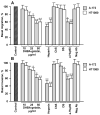
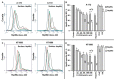
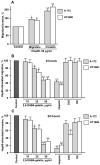
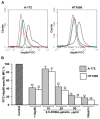
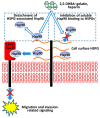
The extracellular cell surface-associated and soluble heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is known to participate in the migration and invasion of tumor cells. Earlier, we demonstrated that plasma membrane-associated heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) bind the extracellular Hsp90 and thereby promote the Hsp90-mediated motility of tumor cells. Here, we showed that a conjugate of 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid with gelatin (2,5-DHBA-gelatin), a synthetic polymer with heparin-like properties, suppressed the basal (unstimulated) migration and invasion of human glioblastoma A-172 and fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells, which was accompanied by the detachment of a fraction of Hsp90 from cell surface HSPGs. The polymeric conjugate also inhibited the migration/invasion of cells stimulated by exogenous soluble native Hsp90, which correlated with the inhibition of the attachment of soluble Hsp90 to cell surface HSPGs. The action of the 2,5-DHBA-gelatin conjugate on the motility of A-172 and HT1080 cells was similar to that of heparin. The results demonstrate a potential of the 2,5-DHBA-gelatin polymer for the development of antimetastatic drugs targeting cell motility and a possible role of extracellular Hsp90 in the suppression of the migration and invasion of tumor cells mediated by the 2,5-DHBA-gelatin conjugate and heparin.
Keywords: 2,5-DHBA–gelatin conjugate; 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (2,5-DHBA); cell migration and invasion; extracellular Hsp90; heparin-like polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are involved in the extracellular Hsp90-stimulated migration and invasion of cancer cells.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2019 Mar;24(2):309-322. doi: 10.1007/s12192-018-0955-5. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2019. PMID: 30659446 Free PMC article.
-
Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are involved in the binding of Hsp90α and Hsp90β to the cell plasma membrane.Cell Adh Migr. 2015;9(6):460-8. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2015.1103421. Cell Adh Migr. 2015. PMID: 26651243 Free PMC article.
-
[The Role of Membrane-Bound Heat Shock Proteins Hsp90 in Migration of Tumor Cells in vitro and Involvement of Cell Surface Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in Protein Binding to Plasma Membrane].Biofizika. 2016 Mar-Apr;61(2):328-36. Biofizika. 2016. PMID: 27192836 Russian.
-
[Mechanism of tumor cell-induced extracellular matrix degradation--inhibition of cell-surface proteolytic activity might have a therapeutic effect on tumor cell invasion and metastasis].Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 Aug;48(8):623-32. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8808830 Review. Japanese.
-
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and heparin regulate melanoma cell functions.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1840(8):2471-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.01.031. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24486410 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive Value of Serum Heat Shock Protein 90α on the Prognosis of Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Mar 16;16:1183-1193. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S401444. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 36960296 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the structures, mechanisms and targeting of molecular chaperones.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Mar 12;10(1):84. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02166-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40069202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Colorectal Cancer Prevention by Aspirin-A Literature Review and Perspective on the Role of COX-Dependent and -Independent Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 27;21(23):9018. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239018. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33260951 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

