The Dual-Active Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist and Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitor E100 Alleviates Autistic-Like Behaviors and Oxidative Stress in Valproic Acid Induced Autism in Mice
- PMID: 32503208
- PMCID: PMC7312782
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21113996
The Dual-Active Histamine H3 Receptor Antagonist and Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitor E100 Alleviates Autistic-Like Behaviors and Oxidative Stress in Valproic Acid Induced Autism in Mice
Abstract
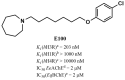
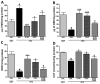
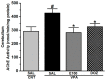
The histamine H3 receptor (H3R) functions as auto- and hetero-receptors, regulating the release of brain histamine (HA) and acetylcholine (ACh), respectively. The enzyme acetylcholine esterase (AChE) is involved in the metabolism of brain ACh. Both brain HA and ACh are implicated in several cognitive disorders like Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, anxiety, and narcolepsy, all of which are comorbid with autistic spectrum disorder (ASD). Therefore, the novel dual-active ligand E100 with high H3R antagonist affinity (hH3R: Ki = 203 nM) and balanced AChE inhibitory effect (EeAChE: IC50 = 2 µM and EqBuChE: IC50 = 2 µM) was investigated on autistic-like sociability, repetitive/compulsive behaviour, anxiety, and oxidative stress in male C57BL/6 mice model of ASD induced by prenatal exposure to valproic acid (VPA, 500 mg/kg, intraperitoneal (i.p.)). Subchronic systemic administration with E100 (5, 10, and 15 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly and dose-dependently attenuated sociability deficits of autistic (VPA) mice in three-chamber behaviour (TCB) test (all p < 0.05). Moreover, E100 significantly improved repetitive and compulsive behaviors by reducing the increased percentage of marbles buried in marble-burying behaviour (MBB) (all p < 0.05). Furthermore, pre-treatment with E100 (10 and 15 mg/kg, i.p.) corrected decreased anxiety levels (p < 0.05), however, failed to restore hyperactivity observed in elevated plus maze (EPM) test. In addition, E100 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) mitigated oxidative stress status by increasing the levels of decreased glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT), and decreasing the elevated levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) in the cerebellar tissues (all p < 0.05). Additionally, E100 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly reduced the elevated levels of AChE activity in VPA mice (p < 0.05). These results demonstrate the promising effects of E100 on in-vivo VPA-induced ASD-like features in mice, and provide evidence that a potent dual-active H3R antagonist and AChE inhibitor (AChEI) is a potential drug candidate for future therapeutic management of autistic-like behaviours.
Keywords: E100; VPA-induced autism-like behaviors; acetylcholine esterase inhibitor; antagonist; anxiety histamine H3R; cerebellum; mice; oxidative stress; repetitive behaviors; sociability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

