Osteomeles schwerinae Extract and Its Major Compounds Inhibit Methylglyoxal-Induced Apoptosis in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 32503323
- PMCID: PMC7321095
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25112605
Osteomeles schwerinae Extract and Its Major Compounds Inhibit Methylglyoxal-Induced Apoptosis in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
Abstract
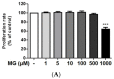
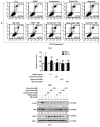
The accumulation and formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are related to diabetes and age-related disease. Osteomeles schwerinae C. K. Schneid. (Rosaceae, OSSC) is used traditionally for the treatment of various diseases in Asia. Previous studies have shown that OSSC elicits preventive effects in an in vivo model of diabetes. This study was to evaluate the antiapoptotic effects of dried leaves and twigs of OSSC extract and its major compounds in ARPE-19 cells-spontaneously arising human retinal pigment epithelial cells-under diabetic conditions. To examine the effects of an OSSC extract and its active compounds (acetylvitexin, hyperoside and quercitrin) on apoptosis in methylglyoxal (MG, the active precursor in the formation of AGEs)-treated ARPE-19 cells and the mechanism by which these effects occur, apoptosis was measured using flow cytometry analysis. Protein expression levels of phospho-p53 (p-p53), Bax and Bcl-2 were determined by western blot analyses. The OSSC extract inhibited apoptosis in MG-treated ARPE-19 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The major compounds also reduced the rate of apoptosis. Both the extract and major compounds also inhibited the expression of p-p53 and Bax and increased the levels of Bcl-2 that had been previously reduced by MG treatment. The OSSC extract (0.1 μg/mL) and its major compounds (0.01 μM) attenuated apoptosis in ARPE-19 cells under toxic diabetic conditions by downregulating of expression of p-p53 and Bax. OSSC may serve as an alternative therapy to retard the development of diabetic retinopathy.
Keywords: Osteomeles schwerinae; apoptosis; diabetic retinopathy; human retinal pigment epithelial cells; methylglyoxal.
Conflict of interest statement
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there was no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Osteomeles schwerinae extracts inhibits the binding to receptors of advanced glycation end products and TGF-β1 expression in mesangial cells under diabetic conditions.Phytomedicine. 2016 Apr 15;23(4):388-97. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Feb 21. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27002409
-
Improvement in Diabetic Retinopathy through Protection against Retinal Apoptosis in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii Rats Mediated by Ethanol Extract of Osteomeles schwerinae C.K. Schneid.Nutrients. 2019 Mar 4;11(3):546. doi: 10.3390/nu11030546. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30836664 Free PMC article.
-
Osteomeles schwerinae Extract Prevents Diabetes-Induced Renal Injury in Spontaneously Diabetic Torii Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Apr 24;2018:6824215. doi: 10.1155/2018/6824215. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29849722 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of puerariae radix extract and its single compounds on methylglyoxal-induced apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Mar 28;152(3):594-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Jan 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24486213
-
Anti-glycation and anti-angiogenic activities of 5'-methoxybiphenyl-3,4,3'-triol, a novel phytochemical component of Osteomeles schwerinae.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Aug 5;760:172-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.04.022. Epub 2015 Apr 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25917323
Cited by
-
Alu antisense RNA ameliorates methylglyoxal-induced human lens epithelial cell apoptosis by enhancing antioxidant defense.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Feb 18;16(2):178-190. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.02.03. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36816207 Free PMC article.
-
The Herbal Combination CPA4-1 Inhibits Changes in Retinal Capillaries and Reduction of Retinal Occludin in db/db Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jul 16;9(7):627. doi: 10.3390/antiox9070627. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32708791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goh S.Y., Cooper M.E. Clinical review: The role of advanced glycation end products in progression and complications of diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes. 2008;93:1143–1152. - PubMed
-
- Cai J., Nelson K.C., Wu M., Sternberg P., Jr., Jones D.P. Oxidative damage and protection of the RPE. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2000;19:205–221. - PubMed
-
- Wang P., Xing Y., Chen C., Chen Z., Qian Z. Advanced glycation end-product (AGE) induces apoptosis in human retinal ARPE-19 cells via promoting mitochondrial dysfunction and activating the Fas-FasL signaling. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016;80:250–256. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2015.1095065. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

