Tübingen hip flexion splints for developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants aged 0-6 months
- PMID: 32503452
- PMCID: PMC7275443
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-020-02171-0
Tübingen hip flexion splints for developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants aged 0-6 months
Abstract
Background: Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) is a common disorder in infants. The present study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the Tübingen hip flexion splints in treating DDH in infants aged 0-6 months.
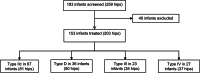
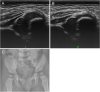
Methods: This is a retrospective study analyzing 259 hips in 195 infants with DDH of Graf type IIc or worse classifications treated between January 2015 and December 2017. Patients were followed up for at least 6 months. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head was diagnosed using plain radiographs at the last follow-up visit according to the Bucholz-Ogden classification. Successful treatment was defined as an improvement of the Graft classification to type I, or an improvement of the International Hip Dysplasia Institute classification to type I in patients aged > 6 months.
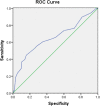
Results: Treatment was deemed successful in 128 patients (83.7%). Avascular necrosis occurred in 3 patients (3 hips). Univariate analysis showed that late treatment initiation, family history of DDH, Graf type IV and bilateral involvement were independent risk factors for treatment failure (p < 0.05). The receiver operating characteristic curve showed a cut-off value of 12 weeks for age at treatment initiation regarding successful treatment. Logistic regression analysis showed that gender, breech presentation, firstborn, swaddling, birth weight > 3.5 kg, oligohydramnios, foot deformity and torticollis did not affect the success rate of treatment (p > 0.05).
Conclusions: The Tübingen splint showed good efficacy and safety in treating DDH in infants aged 0-6 months. Family history of DDH, Graf classification of type IV, bilateral involvement and treatment initiation after 12 weeks of age are risk factors of treatment failure.
Trial registration: N/A.
Keywords: Developmental dysplasia of the hip; Graf classification; Tübingen splint; Ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Morello P. Clinical practice guideline: early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Committee on quality improvement, subcommittee on developmental dysplasia of the hip. American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics. 2000;105(4 Pt 1):896–905. - PubMed
-
- Aronson J. Osteoarthritis of the young adult hip: etiology and treatment. Instr Course Lect. 1986;35:119–128. - PubMed
-
- Furnes O, Lie SA, Espehaug B, Vollset SE, Engesaeter LB, Havelin LI. Hip disease and the prognosis of total hip replacements. A review of 53,698 primary total hip replacements reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty register 1987-99. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2001;83:579–586. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.83B4.0830579. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

