Iridoid glycosides from Morinda officinalis How. exert anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects through inactivating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways
- PMID: 32503513
- PMCID: PMC7275542
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-020-02895-7
Iridoid glycosides from Morinda officinalis How. exert anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects through inactivating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways
Abstract
Background: The root of Morinda officinalis How. (MO, the family of Rubiaceae) has long been used to treat inflammatory diseases in China and other eastern Asian countries, and iridoid glycosides extracted from MO (MOIG) are believed to contribute to this anti-inflammatory effect. However, the mechanism underlying the anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activities of MOIG has not been elucidated. The aim of the present study was to determine how MOIG exerted anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects in vivo and in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
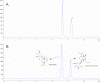
Methods: MOIG were enriched by XDA-1 macroporous resin. The maximum feasible dose method was adopted to evaluate its acute toxicity. The analgesic effect of MOIG was evaluated by acetic acid writhing test and the anti-inflammatory effect was evaluated by cotton-pellet granuloma test in rats and air pouch granuloma test in mice. The anti-arthritic effect was evaluated by establishing an adjuvant arthritis model induced by Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA). The viability of the cultured RAW 264.7 macrophages was assessed by 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The anti-inflammatory activity was evaluated by measuring NO, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α levels in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. The protein level of inflammatory responsive genes was evaluated by Western blot analysis.
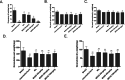
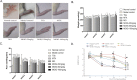
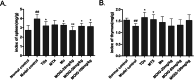
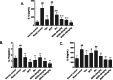
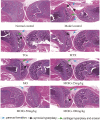
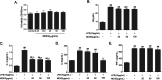
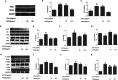
Results: MOIG had no significant toxicity at maximum feasible dose of 22.5 g/kg. MO extracts and MOIG (50,100 and 200 mg/kg) all evoked a significantly inhibitory effects on the frequency of twisting induced by acetic acid in mice compared with the model control group. Administration of MO extracts and MOIG markedly decreased the dry and wet weight of cotton pellet granuloma in rats and air pouch granuloma in mice. MOIG significantly attenuated the paw swelling and decreased the arthritic score, weight loss, spleen index, and the serum level of inflammatory factors IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-17a in CFA-induced arthritic rats. MOIG inhibited the production of inflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, and the expressions of iNOS, COX-2 and proteins related to MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages.
Conclusion: MOIG exerted anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activities through inactivating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, and this finding may provide a sound experimental basis for the clinical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with MOIG.
Keywords: Anti-arthritis; Anti-inflammation; Iridoid glycoside; MAPK pathway; Morinda officinalis how.; NF-κB; RAW 264.7 macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hu Y, Liu X, Xia Q, Yin T, Bai C, Wang Z, Du L, Li X, Wang W, Sun L, Liu Y, Zhang H. Deng L4, Chen Y: comparative anti-arthritic investigation of iridoid glycosides and crocetin derivatives from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis in Freund's complete adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Phytomedicine. 2019;53:223–233. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.07.005. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

