COVID-19: The Potential Role of Copper and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) in a Combination of Candidate Antiviral Treatments Against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32503814
- PMCID: PMC8378025
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11946
COVID-19: The Potential Role of Copper and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) in a Combination of Candidate Antiviral Treatments Against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Background: On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) a pandemic. Since then, thousands of people have suffered and died, making the need for a treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) more crucial than ever.
Materials and methods: The authors carried out a search in PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov and New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) for COVID-19 to provide information on the most promising treatments against SARS-CoV-2.
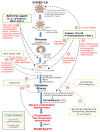
Results: Possible COVID-19 agents with promising efficacy and favorable safety profile were identified. The results support the combination of copper, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), colchicine and nitric oxide (NO) with candidate antiviral agents, remdesivir or EIDD-2801, as a treatment for patients positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Conclusion: The authors propose to study the effects of the combination of copper, NAC, colchicine, NO and currently used experimental antiviral agents, remdesivir or EIDD-2801, as a potential treatment scheme for SARS-COV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; EIDD-2801; N-acetylcysteine (NAC); copper; remdesivir (RDV); review; treatment.
Copyright© 2020, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors have no conflicts of interest regarding this review paper.
Figures
References
-
- Mapping the worldwide spread of the coronavirus 2020. The Washington Post, 2020. Available at: https://www.washingtonpost.com/graphics/2020/world/mapping-spread-new-co... [Last accessed on 10th May, 2020]
-
- de Groot RJ, Baker SC, Baric R, Enjuanes L, Gorbalenya AE, Holmes KV, Perlman S, Poon L, Rottier PJM, Talbot PJ, Woo PCY, Ziebuhr J. King A, Adams M, Carstens E, Lefkowitz E, editors. Family coronaviridae: Part ii – the positive sense single stranded rna viruses. In: Virus taxonomy: Classification and nomenclature of viruses: Ninth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. Elsevier/Academic Press: Amsterdam, Boston. 2012:pp.806.
-
- de Groot RJ, Baker SC, Baric RS, Brown CS, Drosten C, Enjuanes L, Fouchier RAM, Galiano M, Gorbalenya AE, Memish ZA, Perlman S, Poon LLM, Snijder EJ, Stephens GM, Woo PCY, Zaki AM, Zambon M, Ziebuhr J. Middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (mers-cov): Announcement of the coronavirus study group. J Virol. 2013 doi: 10.1128/jvi.01244-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous