Breast Cancer and COVID-19: The Effect of Fear on Patients' Decision-making Process
- PMID: 32503825
- PMCID: PMC8378027
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11957
Breast Cancer and COVID-19: The Effect of Fear on Patients' Decision-making Process
Abstract
Background/aim: Coronavirus-19 (COVID-19) pandemic outbreak is currently having a huge impact on medical resource allocation. Breast Cancer (BC) patients are concerned both with BC treatment and COVID-19. This study aimed to estimate the impact of anxiety among patients, caused by the spreading of COVID-19.
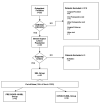
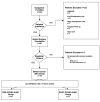
Patients and methods: Between the 16th of January and the 20th of March 2020, we retrospectively enrolled 160 patients. Eighty-two patients with a suspected breast lesion (SBL) were divided into two groups: PRE-COVID-19-SBL and POST-COVID-19-SBL. Seventy-eight BC patients were divided into PRE-COVID-19-BC and POST-COVID-19-BC. Patient characteristics including age, marital status, SBL/BC diameter, personal and family history of BC, clinical stage and molecular subtype were recorded. Procedure Refusal (PR) and Surgical Refusal (SR) were also recorded with their reason.
Results: BC and SBL analysis showed no difference in pre-treatment characteristics (p>0.05). Both POST-COVID-19-SBL and POST-COVID-19-BC groups showed higher rates of PR and SR (p=0.0208, p=0.0065 respectively). Infection risk represented primary reason for refusal among POST-COVID-19 patients.
Conclusion: COVID-19-related anxiety could affect patients' decision-making process.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-SOV-2; anxiety; breast cancer; decision-making process; surgery; surgery refusal.
Copyright© 2020, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this study.
Figures
References
-
- Situation Report-60 SITUATION IN NUMBERS total (new) cases in last 24 hours WHO RISK ASSESSMENT Global Level Very High. Available at: https://www.who.int/docs/defaultsource/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20.... [Last accessed March 21, 2020]
-
- Chan JFW, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KKW, Chu H, Yang J, Xing F, Liu J, Yip CCY, Poon RWS, Tsoi HW, Lo SKF, Chan KH, Poon VKM, Chan WM, Ip JD, Cai JP, Cheng VCC, Chen H, Hui CKM, Yuen KY. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020;395:514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous