SETDB1 is required for intestinal epithelial differentiation and the prevention of intestinal inflammation
- PMID: 32503845
- PMCID: PMC7873423
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321339
SETDB1 is required for intestinal epithelial differentiation and the prevention of intestinal inflammation
Abstract
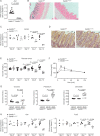
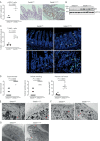
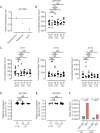
Objective: The intestinal epithelium is a rapidly renewing tissue which plays central roles in nutrient uptake, barrier function and the prevention of intestinal inflammation. Control of epithelial differentiation is essential to these processes and is dependent on cell type-specific activity of transcription factors which bind to accessible chromatin. Here, we studied the role of SET Domain Bifurcated Histone Lysine Methyltransferase 1, also known as ESET (SETDB1), a histone H3K9 methyltransferase, in intestinal epithelial homeostasis and IBD.
Design: We investigated mice with constitutive and inducible intestinal epithelial deletion of Setdb1, studied the expression of SETDB1 in patients with IBD and mouse models of IBD, and investigated the abundance of SETDB1 variants in healthy individuals and patients with IBD.
Results: Deletion of intestinal epithelial Setdb1 in mice was associated with defects in intestinal epithelial differentiation, barrier disruption, inflammation and mortality. Mechanistic studies showed that loss of SETDB1 leads to de-silencing of endogenous retroviruses, DNA damage and intestinal epithelial cell death. Predicted loss-of-function variants in human SETDB1 were considerably less frequently observed than expected, consistent with a critical role of SETDB1 in human biology. While the vast majority of patients with IBD showed unimpaired mucosal SETDB1 expression, comparison of IBD and non-IBD exomes revealed over-representation of individual rare missense variants in SETDB1 in IBD, some of which are predicted to be associated with loss of function and may contribute to the pathogenesis of intestinal inflammation.
Conclusion: SETDB1 plays an essential role in intestinal epithelial homeostasis. Future work is required to investigate whether rare variants in SETDB1 contribute to the pathogenesis of IBD.
Keywords: IBD; IBD - genetics; epithelial differentiation; gut inflammation; intestinal epithelium.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
