Inhibition of Bruton tyrosine kinase in patients with severe COVID-19
- PMID: 32503877
- PMCID: PMC7274761
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abd0110
Inhibition of Bruton tyrosine kinase in patients with severe COVID-19
Abstract
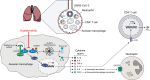
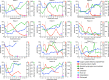
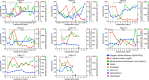
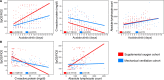
Patients with severe COVID-19 have a hyperinflammatory immune response suggestive of macrophage activation. Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) regulates macrophage signaling and activation. Acalabrutinib, a selective BTK inhibitor, was administered off-label to 19 patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 (11 on supplemental oxygen; 8 on mechanical ventilation), 18 of whom had increasing oxygen requirements at baseline. Over a 10-14 day treatment course, acalabrutinib improved oxygenation in a majority of patients, often within 1-3 days, and had no discernable toxicity. Measures of inflammation - C-reactive protein and IL-6 - normalized quickly in most patients, as did lymphopenia, in correlation with improved oxygenation. At the end of acalabrutinib treatment, 8/11 (72.7%) patients in the supplemental oxygen cohort had been discharged on room air, and 4/8 (50%) patients in the mechanical ventilation cohort had been successfully extubated, with 2/8 (25%) discharged on room air. Ex vivo analysis revealed significantly elevated BTK activity, as evidenced by autophosphorylation, and increased IL-6 production in blood monocytes from patients with severe COVID-19 compared with blood monocytes from healthy volunteers. These results suggest that targeting excessive host inflammation with a BTK inhibitor is a therapeutic strategy in severe COVID-19 and has led to a confirmatory international prospective randomized controlled clinical trial.
Copyright © 2020, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
References
-
- Lu R., Zhao X., Li J., Niu P., Yang B., Wu H., Wang W., Song H., Huang B., Zhu N., Bi Y., Ma X., Zhan F., Wang L., Hu T., Zhou H., Hu Z., Zhou W., Zhao L., Chen J., Meng Y., Wang J., Lin Y., Yuan J., Xie Z., Ma J., Liu W. J., Wang D., Xu W., Holmes E. C., Gao G. F., Wu G., Chen W., Shi W., Tan W., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 395, 565–574 (2020). 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guan W. J., Ni Z. Y., Hu Y., Liang W. H., Ou C. Q., He J. X., Liu L., Shan H., Lei C. L., Hui D. S. C., Du B., Li L. J., Zeng G., Yuen K. Y., Chen R. C., Tang C. L., Wang T., Chen P. Y., Xiang J., Li S. Y., Wang J. L., Liang Z. J., Peng Y. X., Wei L., Liu Y., Hu Y. H., Peng P., Wang J. M., Liu J. Y., Chen Z., Li G., Zheng Z. J., Qiu S. Q., Luo J., Ye C. J., Zhu S. Y., Zhong N. S.; China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19 , Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 1708–1720 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Conti P., Ronconi G., Caraffa A., Gallenga C. E., Ross R., Frydas I., Kritas S. K., Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): Anti-inflammatory strategies. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 34, (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

