Modular gateway-ness connectivity and structural core organization in maritime network science
- PMID: 32503974
- PMCID: PMC7275034
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16619-5
Modular gateway-ness connectivity and structural core organization in maritime network science
Abstract
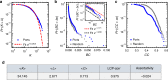
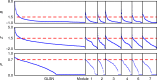
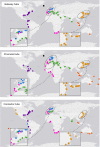
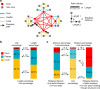
Around 80% of global trade by volume is transported by sea, and thus the maritime transportation system is fundamental to the world economy. To better exploit new international shipping routes, we need to understand the current ones and their complex systems association with international trade. We investigate the structure of the global liner shipping network (GLSN), finding it is an economic small-world network with a trade-off between high transportation efficiency and low wiring cost. To enhance understanding of this trade-off, we examine the modular segregation of the GLSN; we study provincial-, connector-hub ports and propose the definition of gateway-hub ports, using three respective structural measures. The gateway-hub structural-core organization seems a salient property of the GLSN, which proves importantly associated to network integration and function in realizing the cargo transportation of international trade. This finding offers new insights into the GLSN's structural organization complexity and its relevance to international trade.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- UNCTAD. Review of Maritime Transport 2017. https://unctad.org/en/pages/publicationwebflyer.aspx?publicationid=1890 (2017).
-
- Bernhofen DM, El-Sahli Z, Kneller R. Estimating the effects of the container revolution on world trade. J. Int. Econ. 2016;98:36–50.
-
- Limão N, Venables AJ. Infrastructure, geographical disadvantage, transport costs, and trade. World Bank Econ. Rev. 2001;15:451–479.
-
- Clark X, Dollar D, Micco A. Port efficiency, maritime transport costs, and bilateral trade. J. Dev. Econ. 2004;75:417–450.
-
- Bar-Yam Y. Dynamics of Complex Systems. Cambridge, MA: Westview Press; 1997.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

