Circulating miR34a levels as a potential biomarker in the follow-up of Ewing sarcoma
- PMID: 32504411
- PMCID: PMC7511499
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-020-00567-2
Circulating miR34a levels as a potential biomarker in the follow-up of Ewing sarcoma
Abstract
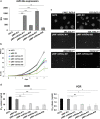
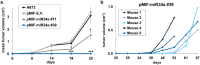
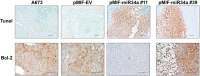
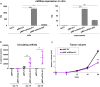
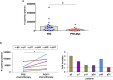
Appropriate tools for monitoring sarcoma progression are still limited. The aim of the present study was to investigate the value of miR-34a-5p (miR34a) as a circulating biomarker to follow disease progression and measure the therapeutic response. Stable forced re-expression of miR34a in Ewing sarcoma (EWS) cells significantly limited tumor growth in mice. Absolute quantification of miR34a in the plasma of mice and 31 patients showed that high levels of this miRNA inversely correlated with tumor volume. In addition, miR34a expression was higher in the blood of localized EWS patients than in the blood of metastatic EWS patients. In 12 patients, we followed miR34a expression during preoperative chemotherapy. While there was no variation in the blood miR34a levels in metastatic patients at the time of diagnosis or after the last cycle of preoperative chemotherapy, there was an increase in the circulating miR34a levels in patients with localized tumors. The three patients with the highest fold-increase in the miR levels did not show evidence of metastasis. Although this analysis should be extended to a larger cohort of patients, these findings imply that detection of the miR34a levels in the blood of EWS patients may assist with the clinical management of EWS.
Keywords: Circulating biomarkers; Ewing sarcoma; Metastases; miR34a; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures

References
-
- Bacci G, Mercuri M, Longhi A, Bertoni F, Barbieri E, Donati D, Giacomini S, Bacchini P, Pignotti E, Forni C, Ferrari S (2002) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for ewing's tumour of bone: recent experience at the rizzoli orthopaedic institute. Eur J Cancer 38(17):2243–2251 - PubMed
-
- Bardelli A, Pantel K (2017) Liquid biopsies, what we do not know (yet). Cancer Cell 31(2):172–179 - PubMed
-
- Bertaina A, Zecca M, Buldini B, Sacchi N, Algeri M, Saglio F, Perotti C, Gallina AM, Bertaina V, Lanino E, Prete A, Barberi W, Tumino M, Favre C, Cesaro S, del Bufalo F, Ripaldi M, Boghen S, Casazza G, Rabusin M, Balduzzi A, Fagioli F, Pagliara D, Locatelli F (2018) Unrelated donor vs hla-haploidentical alpha/beta t-cell- and b-cell-depleted hsct in children with acute leukemia. Blood 132(24):2594–2607 - PubMed
-
- Brohl AS, Solomon DA, Chang W, Wang J, Song Y, Sindiri S, Patidar R, Hurd L, Chen L, Shern JF, Liao H, Wen X, Gerard J, Kim JS, Lopez Guerrero JA, Machado I, Wai DH, Picci P, Triche T, Horvai AE, Miettinen M, Wei JS, Catchpool D, Llombart-Bosch A, Waldman T, Khan J (2014) The genomic landscape of the Ewing sarcoma family of tumors reveals recurrent stag2 mutation. PLoS Genet 10(7):e1004475 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crompton BD, Stewart C, Taylor-Weiner A, Alexe G, Kurek KC, Calicchio ML, Kiezun A, Carter SL, Shukla SA, Mehta SS, Thorner AR, de Torres C, Lavarino C, Sunol M, McKenna A, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Rosenberg M, Ambrogio L, Auclair D, Seepo S, Blumenstiel B, DeFelice M, Imaz-Rosshandler I, Schwarz-Cruz y Celis A, Rivera MN, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Fleming MD, Golub TR, Getz G, Mora J, Stegmaier K (2014) The genomic landscape of pediatric Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Discov 4(11):1326–1341 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

