Dysregulated expression of the alternatively spliced variant mRNAs of the mu opioid receptor gene, OPRM1, in the medial prefrontal cortex of male human heroin abusers and heroin self-administering male rats
- PMID: 32506472
- PMCID: PMC8143898
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.24640
Dysregulated expression of the alternatively spliced variant mRNAs of the mu opioid receptor gene, OPRM1, in the medial prefrontal cortex of male human heroin abusers and heroin self-administering male rats
Abstract
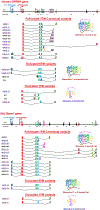
Heroin, a mu agonist, acts through the mu opioid receptor. The mu opioid receptor gene, OPRM1, undergoes extensive alternative splicing, creating an array of splice variants that are conserved from rodent to humans. Increasing evidence suggests that these OPRM1 splice variants are pharmacologically important in mediating various actions of mu opioids, including analgesia, tolerance, physical dependence, rewarding behavior, as well as addiction. In the present study, we examine expression of the OPRM1 splice variant mRNAs in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), one of the major brain regions involved in decision-making and drug-seeking behaviors, of male human heroin abusers and male rats that developed stable heroin-seeking behavior using an intravenous heroin self-administration (SA) model. The results show similar expression profiles among multiple OPRM1 splice variants in both human control subjects and saline control rats, illustrating conservation of OPRM1 alternative splicing from rodent to humans. Moreover, the expressions of several OPRM1 splice variant mRNAs were dysregulated in the postmortem mPFCs from heroin abusers compared to the control subjects. Similar patterns were observed in the rat heroin SA model. These findings suggest potential roles of the OPRM1 splice variants in heroin addiction that could be mechanistically explored using the rat heroin SA model.
Keywords: OPRM1; heroin; medial prefrontal cortex; mu opioid receptor; opioid; splicing.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement:
YXP is a co-scientific founder of Sparian Biosciences.
Figures



References
-
- Abbadie C, Gultekin SH, & Pasternak GW (2000). Immunohistochemical localization of the carboxy terminus of the novel mu opioid receptor splice variant MOR-1C within the human spinal cord. Neuroreport, 11, 1953–1957. - PubMed
-
- Abbadie C, Pan YX, Drake CT, & Pasternak GW (2000). Comparative immunohistochemical distributions of carboxy terminus epitopes from the mu-opioid receptor splice variants MOR-1D, MOR-1 and MOR-1C in the mouse and rat CNS. Neuroscience, 100(1), 141–153. - PubMed
-
- Abbadie C, Pan YX, & Pasternak GW (2000). Differential distribution in rat brain of mu opioid receptor carboxy terminal splice variants MOR-1C-like and MOR-1-like immunoreactivity: Evidence for region-specific processing. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 419(2), 244–256. - PubMed
-
- Abbadie C, & Pasternak GW (2001). Differential in vivo internalization of MOR-1 and MOR-1C by morphine. Neuroreport, 12, 3069–3072. - PubMed
-
- Abbadie C, Pasternak GW, & Aicher SA (2001). Presynaptic localization of the carboxy-terminus epitopes of the [mu] opioid receptor splice variants MOR-1C and MOR-1D in the superficial laminae of the rat spinal cord. Neuroscience, 106(4), 833–842. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DA042888/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA042888/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA015446/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA046714/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA015446/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA015446/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007242/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA007242/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA046714/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA007242/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA007242/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

