Safety guidelines for nonsurgical facial procedures during COVID-19 outbreak
- PMID: 32506541
- PMCID: PMC7300825
- DOI: 10.1111/jocd.13530
Safety guidelines for nonsurgical facial procedures during COVID-19 outbreak
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021 Jan;20(1):368. doi: 10.1111/jocd.13848. Epub 2020 Dec 12. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33350090 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic is expected to last for an extended time, making strict safety precautions for office procedures unavoidable. The lockdown is going to be lifted in many areas, and strict guidelines detailing the infection control measures for aesthetic clinics are going to be of particular importance.
Methods: A virtual meeting was conducted with the members (n = 12) of the European Academy of Facial Plastic Surgery Focus Group to outline the safety protocol for the nonsurgical facial aesthetic procedures for aesthetic practices in order to protect the clinic staff and the patients from SARS-CoV-2 infection. The data analysis was undertaken by thematic and iterative approach.
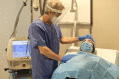
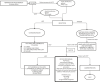
Results: Consensus guidelines for nonsurgical facial aesthetic procedures based on current knowledge are provided for three levels: precautions before visiting the clinic, precautions during the clinic visit, and precautions after the clinic visit.
Conclusions: Sound infection control measures are mandatory for nonsurgical aesthetic practices all around the world. These may vary from country to country, but this logical approach can be customized according to the respective country laws and guidelines.
Keywords: COVID-19; aesthetic clinic; aesthetic medicine; consensus guidelines; coronavirus.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals, LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures






References
-
- World Health Organization . Rolling updates on coronavirus disease (COVID‐19). https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel‐coronavirus‐2019/events‐a.... Accessed March 29, 2020
-
- Italian Ministry of Health , Updates on coronavirus infection. http://www.salute.gov.it/portale/nuovocoronavirus/dettaglioContenutiNuov.... Accessed April 22, 2020
-
- WHO . Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‐19) Situation Reports. April 1 2020. WHO Situat Rep. 2020;2019(72):1‐19.
-
- Kapoor KM, Kapoor A. Role of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of COVID‐19 infection – a systematic literature review. medRxiv. 2020; 2020.03.24.20042366.1:1–12.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

