RNA sequencing of plasma exosomes revealed novel functional long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 32506598
- PMCID: PMC7469810
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.14516
RNA sequencing of plasma exosomes revealed novel functional long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
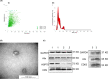
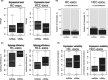
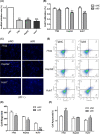
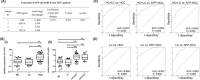
Exosomal long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) has been found to be associated with the development of cancers. However, the expression characteristics and the biological roles of exosomal lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain unknown. Here, by RNA sequencing, we found 9440 mRNAs and 8572 lncRNAs were differentially expressed (DE-) in plasma exosomes between HCC patients and healthy controls. Exosomal DE-lncRNAs displayed higher expression levels and tissue specificity, lower expression variability and splicing efficiency than DE-mRNAs. Six candidate DE-lncRNAs (fold change 6 or more, P ≤ .01) were high in HCC cells and cell exosomes. The knockdown of these candidate DE-lncRNAs significantly affected the migration, proliferation, and apoptosis in HCC cells. In particular, a novel DE-lncRNA, RP11-85G21.1 (lnc85), promoted HCC cellular proliferation and migration by targeted binding and regulating of miR-324-5p. More importantly, the level of serum lnc85 was highly expressed in both Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)-positive and AFP-negative HCC patients and allowed distinguishing AFP-negative HCC from healthy control and liver cirrhosis (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, 0.869; sensitivity, 80.0%; specificity, 76.5%) with high accuracy. Our finding offers a new insight into the association between the dysregulation of exosomal lncRNA and HCC, suggesting that lnc85 could be a potential biomarker of HCC.
Keywords: RP11-85G21.1; hepatocellular carcinoma; long noncoding RNA; miR-324-5p; plasma exosome.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J, de Guevara LL. The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: a global and regional perspective. Oncologist. 2010;15(Suppl 4):5‐13. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69‐90. - PubMed
-
- Chiang JK, Koo M, Kuo TB, Fu CH. Association between cardiovascular autonomic functions and time to death in patients with terminal hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2010;39:673‐679. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Xie X, Xiao YF, et al. The emergence of long non‐coding RNAs in the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2015;360:119‐124. - PubMed
-
- Chen JG, Zhang SW. Liver cancer epidemic in China: past, present and future. Semin Cancer Biol. 2011;21:59‐69. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81760612/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81572908/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- KQCX2015032416521307 JCYJ20160427105140594/Science and Innovation Committee of Shenzhen Municipality
- 2018GXNSFAA281165/Science and Technology Department of Guangxi
- ZY1949025/Science and Technology Department of Guangxi
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

