Covid-19: the renin-angiotensin system imbalance hypothesis
- PMID: 32507883
- PMCID: PMC7276636
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20200492
Covid-19: the renin-angiotensin system imbalance hypothesis
Abstract
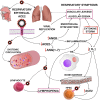
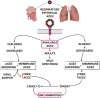
The emergency of SARS-CoV-2 in China started a novel challenge to the scientific community. As the virus turns pandemic, scientists try to map the cellular mechanisms and pathways of SARS-CoV-2 related to the pathogenesis of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19). After transmembrane angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) has been found to be SARS-CoV-2 receptor, we hypothesized an immune-hematological mechanism for Covid-19 based on renin-angiotensin system (RAS) imbalance to explain clinical, laboratory and imaging findings on disease course. We believe that exaggerated activation of ACE/Angiotensin II (Ang II)/Angiotensin Type 1 (AT1) receptor RAS axis in line with reduction of ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor may exert a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of Covid-19. In this perspective, we discuss potential mechanisms and evidence on this hypothesis.
Keywords: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2; Covid-19; Renin-Angiotensin System; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Nair H., Nokes D., Gessner B., Dherani M., Madhi S., Singleton R. et al. . (2010) Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet North Am. Ed. 375, 1545–1555 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60206-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

