The effects of NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition by MCC950 on LPS-induced pancreatic adenocarcinoma inflammation
- PMID: 32507974
- PMCID: PMC11804369
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-020-03274-y
The effects of NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition by MCC950 on LPS-induced pancreatic adenocarcinoma inflammation
Abstract
Purpose: Pancreatic cancer is a lethal form of cancer that can be triggered by prolonged or acute inflammation of the pancreas. Inflammation have been shown to be regulated by a group of key protein molecules known as the inflammasomes. The NLRP3 inflammasome is the most studied inflammasome and have been strongly implicated to regulate cancer cell proliferation. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome under LPS-induced inflammation and its role in modulating cell proliferation in a panel of pancreatic cancer cells.
Methods: The effects of LPS-induced NLRP3 activation in the presence or absence of MCC950, NLRP3-specific inhibitor, was tested on a panel of three pancreatic cancer cell lines (SW1990, PANC1 and Panc10.05). Western blotting, cell viability kits and ELISA kits were used to examine the effects of LPS-induced NLRP3 activation and inhibition by MCC950 on NLRP3 expression, cell viability, caspase-1 activity and cytokine IL-1β, respectively.
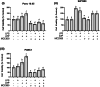
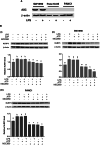
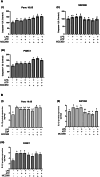
Results: LPS-induced inflammation in the presence of ATP activates NLRP3 that subsequently increases pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by increasing caspase-1 activity leading to overall production of IL-1β. The inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the specific NLRP3 antagonist MCC950 was able to reduce the cell viability of pancreatic cancer cells. However, the efficacy of MCC950 varies between cell types which is most probably due to the difference in ASC expressions which have a different role in inflammasome activation.
Conclusion: There is a dynamic interaction between inflammasome that regulates inflammasome-mediated inflammation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.
Keywords: Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein (ASC); LPS-induced inflammation; MCC950; NLPR3 inflammasome inhibitor; NLRP3 inflammasome; Pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of microglia priming by NLRP3 reduces the impact of early life stress and mild TBI.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Jul 17;22(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03512-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40676661 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Resveratrol on LPS/ATP-induced pyroptosis and inflammatory response in HT29 cells.Autoimmunity. 2024 Dec;57(1):2427094. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2024.2427094. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Autoimmunity. 2024. PMID: 39534992
-
Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation to Alleviate Retinal Inflammation and Protect the Optic Nerve of OPTN(E50K)Mice.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):2105-2121. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02178-0. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39578308 Free PMC article.
-
Target of MCC950 in Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: a Literature Review.Inflammation. 2020 Feb;43(1):17-23. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01098-8. Inflammation. 2020. PMID: 31646445 Review.
-
Flavonoids regulating NLRP3 inflammasome: a promising approach in alleviating diabetic peripheral neuropathy.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 May;33(5):2231-2262. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01729-7. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40205269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The 'speck'-tacular oversight of the NLRP3-pyroptosis pathway on gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases and tumorigenesis.J Biomed Sci. 2023 Oct 27;30(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00983-7. J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 37891577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The trigger for pancreatic disease: NLRP3 inflammasome.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jul 14;9(1):246. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01550-7. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37452057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of Interferon-Inducible Protein 16 Promotes Progression of Human Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Through Interleukin-1β-Induced Tumor-Associated Macrophage Infiltration in the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 4;9:640786. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.640786. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34150748 Free PMC article.
-
An Exploration of Oral-Gut Pathogens Mediating Immune Escape of Pancreatic Cancer via miR-21/PTEN Axis.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 22;13:928846. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.928846. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35814712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased survival in patients with pancreatic cancer may be associated with an increase in histopathological expression of inflammasome marker NLRP3.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Jan;39(1):35-40. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-617. Epub 2023 Apr 4. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 37057822
References
-
- Ahn KS, Hwang JY, Han H-S, Kim ST, Hwang I, Chun Y-O (2018) The impact of acute inflammation on progression and metastasis in pancreatic cancer animal model. Surg Oncol 27:61–69 - PubMed
-
- Chauhan R, Trivedi V (2020) Inflammatory markers in cancer: potential resources. Front Biosci Sch 12:1–24 - PubMed
-
- Coll RC, Hill JR, Day CJ, Zamoshnikova A, Boucher D, Massey NL, Chitty JL, Fraser JA, Jennings MP, Robertson AAB et al (2019) MCC950 directly targets the NLRP3 ATP-hydrolysis motif for inflammasome inhibition. Nat Chem Biol 15:556–559 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

