Physical and physiological demands of basketball small-sided games: the influence of defensive and time pressures
- PMID: 32508380
- PMCID: PMC7249796
- DOI: 10.5114/biolsport.2020.93038
Physical and physiological demands of basketball small-sided games: the influence of defensive and time pressures
Abstract
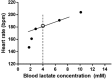
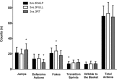
Different small-sided games (SSG) can be used by coaches to induce specific demands on athletes during team sports training. In basketball, defensive and time pressures are common stressors experienced by players during official matches. However, no studies have investigated the effect of changing these variables in SSG during training. We compared the physical and physiological demands of three basketball SSG performed in a half court with two hoops: 3vs3 with man-to-man defence in the half playing area, 3vs3 with man-to-man defence in the full playing area, and 3vs3 with a reduced shot-clock (3vs3HALF, 3vs3FULL, 3vs3RT, respectively). Twelve male U-17 basketball athletes formed four balanced teams. Each team played the three SSG against each other in a random order, totalling 18 SSG. During the SSG, the players wore triaxial accelerometers and heart rate monitors. SSG were filmed to record the players' motor actions. The results showed that 3vs3FULL (p=0.004, d=0.42, small-to-moderate effect) and 3vs3RT (p=0.026, d=0.33, small-to-moderate effect) increased the time spent in higher acceleration zones compared to 3vs3HALF. Both 3vs3FULL and 3vs3RT presented more transition sprints compared to 3vs3HALF. The 3vs3FULL also presented more fakes and the 3vs3RT presented more jumps compared to the 3vs3HALF. Physiological responses presented no differences between the SSG formats. In conclusion, defensive and time pressures increase the physical demand in 3vs3 SSG performed in the half court. The three SSG investigated in this study presented mean heart rate values close to 90% of the maximum heart rate, which suggests that these SSG may be used to increase athletes' aerobic performance.
Keywords: Accelerometer; Defence; External load; Internal load; Shot-clock.
Copyright © Biology of Sport 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors do not have any professional relationships with companies or manufacturers who will benefit from the results of the present study.
Figures
References
-
- Davids K, Araújo D, Correia V, Vilar L. How small-sided and conditioned games enhance acquisition of movement and decision-making skills. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2013;41(3):154–61. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann JJ, Reed JP, Leiting K, Chiang C-Y, Stone M. Repeated Sprints, High Intensity Interval Training, Small Sided Games: Theory and Application to Field Sports. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2014;9(2):352–7. - PubMed
-
- Bredt SGT, Morales JCP, Andrade AGP, Torres JO, Peixoto GH, Greco PJ, et al. Space Creation Dynamics in Basketball Small-Sided Games. Percept Mot Skills [Internet] 2017;125(1):162–76. - PubMed
-
- Clemente FM, Conte D, Sanches R, Moleiro CF, Gomes M, Lima R. Anthropometry and fitness profile, and their relationships with technical performance and perceived effort during small-sided basketball games. Res Sport Med. 2019;27(4):452–66. - PubMed
-
- Klusemann MJ, Pyne DB, Foster C, Drinkwater EJ. Optimising technical skills and physical loading in small-sided basketball games. J Sports Sci. 2012;30(14):1463–71. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
