Serum Concentrations of Cholinesterase Inhibitors in Patients With Alzheimer's Dementia Are Frequently Below the Recommended Levels
- PMID: 32508640
- PMCID: PMC7253642
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00691
Serum Concentrations of Cholinesterase Inhibitors in Patients With Alzheimer's Dementia Are Frequently Below the Recommended Levels
Abstract
Background: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChE-I) are recommended for the treatment of cognitive symptoms but also of behavioral and psychological symptoms in dementia. They are widely used not only in Alzheimer's disease, but also in other forms of dementia. Efficacy of treatment might depend on serum concentration of the respective AChE-I.
Objective: In patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's dementia, we measured serum concentrations of hepatically metabolized donepezil and renally excreted rivastigmine and investigated possible modifiers. Additionally, we looked at correlations between serum concentrations and efficacy for both drugs.
Methods: Serum concentrations of donepezil and rivastigmine were measured by liquid chromatography - tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Allele specific PCR were performed to determine CYP2D6 genotype and gene dose. Clinical efficacy was assessed by changes of the subtest wordlist delayed recall of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease-Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (CERAD-NAB).
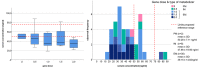
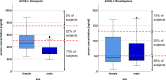
Results: Sixty-seven patients treated with a stable dosage of donepezil 10 mg (n=41) or rivastigmine 9.5 mg (n=26) were included. Mean serum concentration of donepezil and rivastigmine were 41.2 and 6.5 ng/ml, respectively. Serum concentrations were below the recommended range in 73% of the subjects in the donepezil group and in 65% of the participants in the rivastigmine group. When applying a dose-related reference, ranges 63% of patients in the donepezil group and 32% in the rivastigmine group had concentrations below the expected range. Gene dose, sex, and duration of treatment significantly predicted donepezil serum concentration (p=0.046, p=0.001, p=0.030 respectively). Only for rivastigmine did the serum concentration significantly contribute to the regression model predicting changes on the subtest word list delayed recall (β=0.472; p=0.019).
Conclusions: Serum concentrations of about two thirds of the patients were below the recommended range. When not looking at absolute values but at the dose-related reference ranges, these numbers improved but still 32%, respectively 63% of patients had low serum concentrations. High serum concentrations of rivastigmine predicted clinical response to cognition. Therapeutic drug monitoring might help to identify the cause of poor clinical response to cognition and behavioral and psychological symptoms in patients with AChE-I treatment.
Keywords: Alzheimer's dementia; Alzheimer's disease; CYP2D6 polymorphism; cholinesterase inhibitors; gene dose; serum concentration; therapeutic drug monitoring; treatment efficacy.
Copyright © 2020 Ortner, Stange, Schneider, Schroeder, Buerger, Müller, Dorn, Goldhardt, Diehl-Schmid, Förstl, Steimer and Grimmer.
Figures
References
-
- Blesa R., Bullock R., He Y., Bergman H., Gambina G., Meyer J., et al. (2006). Effect of butyrylcholinesterase genotype on the response to rivastigmine or donepezil in younger patients with Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 16, 771–774. 10.1097/01.fpc.0000220573.05714.ac - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boustani M., Campbell N., Munger S., Maidment I., Fox C. (2008). Impact of anticholinergics on the aging brain: a review and practical application. Aging Health 4, 311–320. 10.2217/1745509X.4.3.311 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

