Genetic Evaluation of Patients With Delayed Puberty and Congenital Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: Is it Worthy of Consideration?
- PMID: 32508745
- PMCID: PMC7248176
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00253
Genetic Evaluation of Patients With Delayed Puberty and Congenital Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: Is it Worthy of Consideration?
Abstract
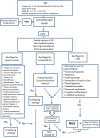
Delayed puberty is a common reason of pediatric endocrinological consultation. It is often a self-limited (or constitutional) condition with a strong familial basis. The type of inheritance is variable but most commonly autosomal dominant. Despite this strong genetic determinant, mutations in genes implicated in the regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis have rarely been identified in cases of self-limited delayed puberty and often in relatives of patients with congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (i.e., FGFR1 and GNRHR genes). However, recently, next-generation sequencing analysis has led to the discovery of new genes (i.e., IGSF10, HS6ST1, FTO, and EAP1) that are implicated in determining isolated self-limited delayed puberty in some families. Despite the heterogeneity of genetic defects resulting in delayed puberty, genetic testing may become a useful diagnostic tool for the correct classification and management of patients with delayed puberty. This article will discuss the benefits and the limitations of genetic testing execution in cases of delayed puberty.
Keywords: genetics; hypogonadal hypogonadism; next-generation sequencing; pediatrics; puberty.
Copyright © 2020 Festa, Umano, Miraglia del Giudice and Grandone.
Figures
References
-
- Varimo T, Miettinen PJ, Kansakoski J, Raivio T, Hero M. Congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, functional hypogonadotropism or constitutional delay of growth and puberty? An analysis of a large patient series from a single tertiary center. Hum Reprod. (2017) 32:147e53 10.1093/humrep/dew294 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous