In vitro and in vivo Effect of Exogenous Farnesol Exposure Against Candida auris
- PMID: 32508780
- PMCID: PMC7251031
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00957
In vitro and in vivo Effect of Exogenous Farnesol Exposure Against Candida auris
Abstract
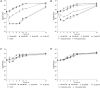
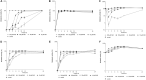
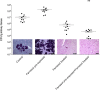
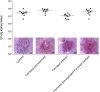
The spreading of multidrug-resistant Candida auris is considered as an emerging global health threat. The number of effective therapeutic regimens is strongly limited; therefore, development of novel strategies is needed. Farnesol is a quorum-sensing molecule with a potential antifungal and/or adjuvant effect; it may be a promising candidate in alternative treatment against Candida species including C. auris. To examine the effect of farnesol on C. auris, we performed experiments focusing on growth, biofilm production ability, production of enzymes related to oxidative stress, triazole susceptibility and virulence. Concentrations ranging from 100 to 300 μM farnesol caused a significant growth inhibition against C. auris planktonic cells for 24 h (p < 0.01-0.05). Farnesol treatment showed a concentration dependent inhibition in terms of biofilm forming ability of C. auris; however, it did not inhibit significantly the biofilm development at 24 h. Nevertheless, the metabolic activity of adhered farnesol pre-exposed cells (75 μM) was significantly diminished at 24 h depending on farnesol treatment during biofilm formation (p < 0.001-0.05). Moreover, 300 μM farnesol exerted a marked decrease in metabolic activity against one-day-old biofilms between 2 and 24 h (p < 0.001). Farnesol increased the production of reactive species remarkably, as revealed by 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein (DCF) assay {3.96 ± 0.89 [nmol DCF (OD640)-1] and 23.54 ± 4.51 [nmol DCF (OD640)-1] for untreated cells and farnesol exposed cells, respectively; p < 0.001}. This was in line with increased superoxide dismutase level {85.69 ± 5.42 [munit (mg protein)-1] and 170.11 ± 17.37 [munit (mg protein)-1] for untreated cells and farnesol exposed cells, respectively; p < 0.001}, but the catalase level remained statistically comparable between treated and untreated cells (p > 0.05). Concerning virulence-related enzymes, exposure to 75 μM farnesol did not influence phospholipase or aspartic proteinase activity (p > 0.05). The interaction between fluconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, isavuconazole and farnesol showed clear synergism (FICI ranges from 0.038 to 0.375) against one-day-old biofilms. Regarding in vivo experiments, daily 75 μM farnesol treatment decreased the fungal burden in an immunocompromised murine model of disseminated candidiasis, especially in case of inocula pre-exposed to farnesol (p < 0.01). In summary, farnesol shows a promising therapeutic or adjuvant potential in traditional or alternative therapies such as catheter lock therapy.
Keywords: biofilm; in vivo; oxidative stress; quorum-sensing; synergy; therapy; triazoles; virulence.
Copyright © 2020 Nagy, Vitális, Jakab, Borman, Forgács, Tóth, Majoros and Kovács.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional Profiling of the Candida auris Response to Exogenous Farnesol Exposure.mSphere. 2021 Oct 27;6(5):e0071021. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00710-21. Epub 2021 Oct 13. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34643421 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptional analysis of Candida auris biofilms following farnesol and tyrosol treatment.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Apr 2;12(4):e0227823. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02278-23. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38440972 Free PMC article.
-
Abrogation of pathogenic attributes in drug resistant Candida auris strains by farnesol.PLoS One. 2020 May 11;15(5):e0233102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233102. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32392266 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Quorum-Sensing Molecules: A Review of Their Antifungal Effect against Candida Biofilms.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Jul 2;6(3):99. doi: 10.3390/jof6030099. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32630687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Properties and role of the quorum sensing molecule farnesol in relation to the yeast Candida albicans.Pharmazie. 2017 Jun 1;72(6):307-312. doi: 10.1691/ph.2017.6174. Pharmazie. 2017. PMID: 29442016 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic Effect of Plant Compounds in Combination with Conventional Antimicrobials against Biofilm of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Candida spp.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 30;16(11):1531. doi: 10.3390/ph16111531. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antifungal lock therapy: an eternal promise or an effective alternative therapeutic approach?Lett Appl Microbiol. 2022 Jun;74(6):851-862. doi: 10.1111/lam.13653. Epub 2022 Jan 30. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35032330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Clues for the Treatment of Fungal Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection With Antifungal Lock Therapy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jan 31;19:683-701. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S501664. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39906698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraspecies heterogeneity in microbial interactions.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2021 Aug;62:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2021.04.003. Epub 2021 May 23. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34034081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of Farnesol with Common Antifungal Drugs: Inhibitory Effect against Candida Species Isolated from Women with RVVC.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Apr 10;59(4):743. doi: 10.3390/medicina59040743. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37109701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agustín M. D. R., Viceconte F. R., Vela Gurovic M. S., Costantino A., Brugnoni L. I. (2019). Effect of quorum sensing molecules and natamycin on biofilms of Candida tropicalis and other yeasts isolated from industrial juice filtration membranes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 126 1808–1820. 10.1111/jam.14248 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

