IL-15 in the Combination Immunotherapy of Cancer
- PMID: 32508818
- PMCID: PMC7248178
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00868
IL-15 in the Combination Immunotherapy of Cancer
Abstract
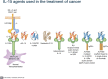
We completed clinical trials of rhIL-15 by bolus, subcutaneous, and continuous intravenous infusions (CIV). IL-15 administered by CIV at 2 mcg/kg/day yielded a 38-fold increase in 10- day number of circulating NK cells, a 358-fold increase in CD56bright NK cells and a 5.8-fold increase in CD8 T cells. However, IL-15 preparations administered as monotherapy were ineffective, due to actions of immunological checkpoints and due to the lack of tumor specific targeting by NK cells. To circumvent checkpoints, trials of IL-15 in combination with other anticancer agents were initiated. Tumor-bearing mice receiving IL-15 with antibodies to CTLA-4 and PD-L1 manifested marked prolongation of survival compared to mice receiving IL-15 with either agent alone. In translation, a phase I trial was initiated involving IL-15 (rhIL-15), nivolumab and ipilimumab in patients with malignancy (NCT03388632). In rhesus macaques CIV IL-15 at 20 μg/kg/day for 10 days led to an 80-fold increase in number of circulating effector memory CD8 T cells. However, administration of γc cytokines such as IL-15 led to paralysis/depression of CD4 T-cells that was mediated through transient expression of SOCS3 that inhibited the STAT5 signaling pathway. This lost CD4 helper role could be restored alternatively by CD40 agonists. In the TRAMP-C2 prostate tumor model the combination of IL-15 with agonistic anti-CD40 produced additive effects in terms of numbers of TRAMP-C2 tumor specific Spas/SCNC/9H tetramer positive CD8 T cells expressed and tumor responses. A clinical trial is being initiated for patients with cancer using an intralesional anti-CD40 in combination with CIV rhIL-15. To translate IL-15-mediated increases in NK cells, we investigated combination therapy of IL-15 with anticancer monoclonal antibodies including rituximab in mouse models of EL-4 lymphoma transfected with human CD20 and with alemtuzumab (CAMPATH-1H) in a xenograft model of adult T cell leukemia (ATL). IL-15 enhanced the ADCC and therapeutic efficacy of both antibodies. These results provided the scientific basis for trials of IL-15 combined with alemtuzumab (anti-CD52) for patients with ATL (NCT02689453), with obinutuzumab (anti-CD20) for patients with CLL (NCT03759184), and with avelumab (anti-PD-L1) in patients with T-cell lymphoma (NCT03905135) and renal cancer (NCT04150562). In the first trial, there was elimination of circulating ATL and CLL leukemic cells in select patients.
Keywords: CD8 T cells; immunological checkpoints; immunotherapy of cancer; interleukin-15; natural killer cells.
Copyright © 2020 Waldmann, Dubois, Miljkovic and Conlon.
Figures
References
-
- Bamford RN, Grant AJ, Burton JD, Peters C, Kurys G, Goldman CK, et al. . The interleukin (IL) 2 receptor beta chain is shared by IL-2 and a cytokine, provisionally designated IL-T, that stimulates T-cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1994) 91:4940–4. 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4940 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burton JD, Bamford RN, Peters C, Grant AJ, Kurys G, Goldman CK, et al. A lymphokine, provisionally designed interleukin T and produced by a human adult T-cell leukemia line, stimulates T-cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (1994) 91:4935–9. 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4935 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

