Development of ImmTOR Tolerogenic Nanoparticles for the Mitigation of Anti-drug Antibodies
- PMID: 32508839
- PMCID: PMC7251066
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00969
Development of ImmTOR Tolerogenic Nanoparticles for the Mitigation of Anti-drug Antibodies
Abstract
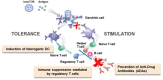
The development of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) is a common cause for treatment failure and hypersensitivity reactions for many biologics. The focus of this review is the development of ImmTOR, a platform technology designed to prevent the formation of ADAs that can be applied broadly across a wide variety of biologics by inducing immunological tolerance with ImmTOR nanoparticles encapsulating rapamycin. The induction of tolerance is antigen-specific and dependent on the incorporation of rapamycin in nanoparticles and the presence of the antigen at the time of administration of ImmTOR. Evidence for the induction of specific immune tolerance vs. general immune suppression is supported by the findings that: (1) ImmTOR induces regulatory T cells specific to the co-administered antigen; (2) tolerance can be transferred by adoptive transfer of splenocytes from treated animals to naïve recipients; (3) the tolerance is durable to subsequent challenge with antigen alone; and (4) animals tolerized to a specific antigen are capable of responding to an unrelated antigen. ImmTOR nanoparticles can be added to new or existing biologics without the need to modify or reformulate the biologic drug. The ability of ImmTOR to mitigate the formation of ADAs has been demonstrated for coagulation factor VIII in a mouse model of hemophilia A, an anti-TNFα monoclonal antibody in a mouse model of inflammatory arthritis, pegylated uricase in hyperuricemic mice and in non-human primates, acid alpha-glucosidase in a mouse model of Pompe disease, recombinant immunotoxin in a mouse model of mesothelioma, and adeno-associated vectors in a model of repeat dosing of gene therapy vectors in mice and in non-human primates. Human proof-of concept for the mitigation of ADAs has been demonstrated with SEL-212, a combination product consisting of ImmTOR + pegadricase, a highly immunogenic enzyme therapy for the treatment of gout. ImmTOR represents a promising approach to preventing the formation of ADAs to a broad range of biologic drugs.
Keywords: anti-drug antibodies; immune tolerance; nanoparticles; rapamycin; regulatory T cells.
Copyright © 2020 Kishimoto.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancement of the Tolerogenic Phenotype in the Liver by ImmTOR Nanoparticles.Front Immunol. 2021 May 25;12:637469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637469. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34113339 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerogenic nanoparticles mitigate the formation of anti-drug antibodies against pegylated uricase in patients with hyperuricemia.Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 12;13(1):272. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27945-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35022448 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin nanoparticles increase the therapeutic window of engineered interleukin-2 and drive expansion of antigen-specific regulatory T cells for protection against autoimmune disease.J Autoimmun. 2023 Nov;140:103125. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103125. Epub 2023 Oct 14. J Autoimmun. 2023. PMID: 37844543
-
Nanoparticles for the Induction of Antigen-Specific Immunological Tolerance.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 20;9:230. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00230. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29515571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerogenic nanoparticles restore the antitumor activity of recombinant immunotoxins by mitigating immunogenicity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 23;115(4):E733-E742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717063115. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29311317 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The COMPARE head-to-head, randomized controlled trial of SEL-212 (pegadricase plus rapamycin-containing nanoparticle, ImmTOR™) versus pegloticase for refractory gout.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Apr 2;63(4):1058-1067. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead333. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37449908 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Enhancement of the Tolerogenic Phenotype in the Liver by ImmTOR Nanoparticles.Front Immunol. 2021 May 25;12:637469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.637469. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34113339 Free PMC article.
-
Rescue of infant progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 mice by repeated dosing of AAV gene therapy.JHEP Rep. 2023 Feb 24;5(5):100713. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100713. eCollection 2023 May. JHEP Rep. 2023. PMID: 37096142 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicines: intervention in inflammatory pathways of cancer.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Jun;31(3):1199-1221. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01217-w. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37060398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The therapeutic potential of immunoengineering for systemic autoimmunity.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024 Apr;20(4):203-215. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01084-x. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38383732 Review.
References
-
- Rosenberg AS. Immunogenicity of biological therapeutics: a hierarchy of concerns. Dev Biol. (2003) 112:15–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources