Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome due to a Novel Compound Heterozygous KCNQ1 Mutation in a Chinese Family
- PMID: 32508908
- PMCID: PMC7246397
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3569359
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome due to a Novel Compound Heterozygous KCNQ1 Mutation in a Chinese Family
Abstract
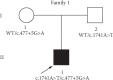
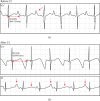
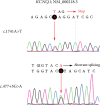
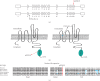
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is a rare but severe autosomal recessive disease characterized by profound congenital deafness and a prolonged QTc interval (greater than 500 milliseconds) in the ECG waveforms. The prevalence of JLNS is about 1/1000000 to 1/200000 around the world. However, exceed 25% of JLNS patients suffered sudden cardiac death with kinds of triggers containing anesthesia. Approximately 90% of JLNS cases are caused by KCNQ1 gene mutations. Here, using next-generation sequencing (NGS), we identified a compound heterozygosity for two mutations c.1741A>T (novel) and c.477+5G>A (known) in KCNQ1 gene as the possible pathogenic cause of JLNS, which suggested a high risk of cardiac events in a deaf child. The hearing of this patient improved significantly with the help of cochlear implantation (CI). But life-threatening arrhythmias occurred with a trigger of anesthesia after the end of the CI surgery. Our findings extend the KCNQ1 gene mutation spectrum and contribute to the management of deaf children diagnosed with JLNS for otolaryngologists (especially cochlear implant teams).
Copyright © 2020 Yue Qiu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

