Size-Optimized Microspace Culture Facilitates Differentiation of Mouse Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Osteoid-Rich Bone Constructs
- PMID: 32508932
- PMCID: PMC7244985
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7082679
Size-Optimized Microspace Culture Facilitates Differentiation of Mouse Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Osteoid-Rich Bone Constructs
Abstract
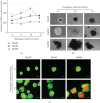
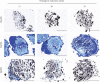
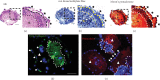
Microspace culture is promising for self-organization of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). However, the optimal size of microspaces for osteogenic differentiation is unclear. We hypothesized that a specific microspace size could facilitate self-organizing iPSC differentiation to form bone-like tissue in vitro. The objectives of this study were to investigate such effects of microspace size and to evaluate bone regeneration upon transplantation of the resulting osteogenic constructs. Dissociated mouse gingival fibroblast-derived iPSCs were plated in ultra-low-attachment microspace culture wells containing hundreds of U-bottom-shaped microwell spots per well to form cell aggregates in growth medium. The microwells had different aperture diameters/depths (400/560 μm (Elp400), 500/700 μm (Elp500), and 900/700 μm (Elp900)) (Kuraray; Elplasia). After 5 days of aggregation, cells were maintained in osteogenic induction medium for 35 days. Only cells in the Elp500 condition tightly aggregated and maintained high viability during osteogenic induction. After 10 days of induction, Elp500 cell constructs showed significantly higher gene expression of Runx2, Osterix, Collagen 1a1, Osteocalcin, Bone sialoprotein, and Osteopontin compared to constructs in Elp400 and Elp900. In methylene blue-counterstained von Kossa staining and Movat's pentachrome staining, only Elp500 constructs showed robust osteoid formation on day 35, with high expression of type I collagen (a major osteoid component) and osteocalcin proteins. Cell constructs were transplanted into rat calvarial bone defects, and micro-CT analysis after 3 weeks showed better bone repair with significantly higher bone mineral density in the Elp500 group compared to the Elp900 group. These results suggest that microspace size affects self-organized osteogenic differentiation of iPSCs. Elp500 microspace culture specifically induces mouse iPSCs into osteoid-rich bone-like tissue possessing high bone regeneration capacity.
Copyright © 2020 Phoonsuk Limraksasin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- O'Brien F. J. Biomaterials & scaffolds for tissue engineering. Materials Today. 2011;14(3):88–95. doi: 10.1016/S1369-7021(11)70058-X. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

