A Systematic Review of In Vitro Activity of Medicinal Plants from Sub-Saharan Africa against Campylobacter spp
- PMID: 32508957
- PMCID: PMC7245682
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9485364
A Systematic Review of In Vitro Activity of Medicinal Plants from Sub-Saharan Africa against Campylobacter spp
Abstract
Introduction: Campylobacter spp. are zoonotic bacteria that cause gastroenteritis in humans and may cause extraintestinal infections such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, reactive arthritis, and bacteremia. Resistance to antibiotics is an increasing concern in the Sub-Saharan Africa; thus, search for alternatives such as plant-based active ingredients is important in order to develop new drugs.
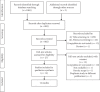
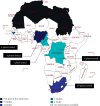
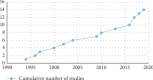
Objectives: To present a systematic review of in vitro and in vivo studies of the antibacterial activity of medicinal plants from Sub-Saharan Africa against Campylobacter spp. Methodology. Studies published until March 2020 on medicinal plants used against Campylobacter spp. from each country of Sub-Saharan Africa were searched on PubMed, Science Direct, AJOL, and Google Scholar. Articles were selected based on the existence of information regarding in vitro and in vivo activity of medicinal plants against Campylobacter spp.
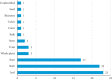
Results: A total of 47 medicinal plants belonging to 28 families were studied for in vitro activity against Campylobacter spp. No plant was studied in vivo. Plants from Fabaceae family were the most commonly studied. The plants with the strongest antimicrobial activities were Cryptolepis sanguinolenta and Terminalia macroptera. The root extracts from these plants were effective, and both had a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 25 μg/ml. Seven pure compounds were isolated and analyzed for activity against Campylobacter spp. The compound cryptolepine from C. sanguinolenta was the most effective with MIC values ranging between 6.25 and 25 μg/ml.
Conclusion: Several native plants from the Sub-Saharan Africa region were studied for in vitro activity against Campylobacter spp. Some plants seemed very effective against the bacteria. Chemical compounds from three plants have been isolated and analyzed, but further studies are needed in order to produce new and effective drugs.
Copyright © 2020 Delfina Fernandes Hlashwayo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

