Association between Timing of Surgical Intervention and Mortality in 15,813 Acute Pancreatitis
- PMID: 32508973
- PMCID: PMC7246404
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/1012796
Association between Timing of Surgical Intervention and Mortality in 15,813 Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
Objective: In order to find the quantitative relationship between timing of surgical intervention and risk of death in necrotizing pancreatitis.
Methods: The generalized additive model was applied to quantitate the relationship between surgical time (from the onset of acute pancreatitis to first surgical intervention) and risk of death adjusted for demographic characteristics, infection, organ failure, and important lab indicators extracted from the Electronic Medical Record of West China Hospital of Sichuan University.
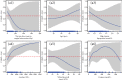
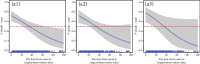
Results: We analyzed 1,176 inpatients who had pancreatic drainage, pancreatic debridement, or pancreatectomy experience of 15,813 acute pancreatitis retrospectively. It showed that when surgical time was either modelled alone or adjusted for infection or organ failure, an L-shaped relationship between surgical time and risk of death was presented. When surgical time was within 32.60 days, the risk of death was greater than 50%.
Conclusion: There is an L-shaped relationship between timing of surgical intervention and risk of death in necrotizing pancreatitis.
Copyright © 2020 Lan Lan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

