EEG Signal and Feature Interaction Modeling-Based Eye Behavior Prediction Research
- PMID: 32508975
- PMCID: PMC7246416
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2801015
EEG Signal and Feature Interaction Modeling-Based Eye Behavior Prediction Research
Abstract
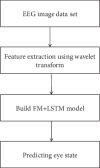
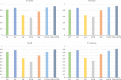
In recent years, with the development of brain science and biomedical engineering, as well as the rapid development of electroencephalogram (EEG) signal analysis methods, using EEG signals to monitor human health has become a very popular research field. The innovation of this paper is to analyze the EEG signal for the first time by building a depth factorization machine model, so that on the basis of analyzing the characteristics of user interaction, we can use EEG data to predict the binomial state of eyes (open eyes and closed eyes). The significance of the research is that we can diagnose the fatigue and the health of the human body by detecting the state of eyes for a long time. On the basis of this inference, the proposed method can make a further useful auxiliary support for improving the accuracy of the recommendation system recommendation results. In this paper, we first extract the features of EEG data by wavelet transform technology and then build a depth factorization machine model (FM+LSTM) which combines factorization machine (FM) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) in parallel. Through the test of real data set, the proposed model gets more efficient prediction results than other classifier models. In addition, the model proposed in this paper is suitable not only for the determination of eye features but also for the acquisition of interactive features (user fatigue) in the recommendation system. The conclusion obtained in this paper will be an important factor in the determination of user preferences in the recommendation system, which will be used in the analysis of interactive features by the graph neural network in the future work.
Copyright © 2020 Pengcheng Ma and Qian Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Gevins A. Hans Berger was right: what I have learned about thinking from the EEG in the past twenty years. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology. 1997;103(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/S0013-4694(97)87921-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical