Dynamics of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 32508995
- PMCID: PMC7271728
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.8572
Dynamics of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Dynamics of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Oct;20(4):3894. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9127. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32905209 Free PMC article.
Abstract
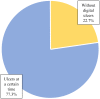
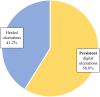
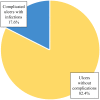
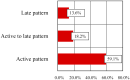
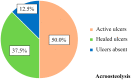
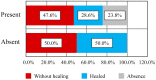
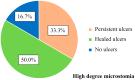
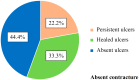
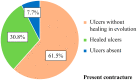
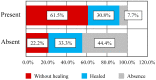
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a collagenosis with insufficiently known etiopathogenesis, characterized by microvasculopathy and excessive fibrosis in the context of an autoimmune disorder. The incompletely elucidated pathogenesis and limited therapeutic options, disabling aspects, skin lesions and pain determine important functional and psychological deficiencies which affect the quality of life. It is imperative to observe and correlate individual clinical and paraclinical data to optimize disease management. A group of 22 patients diagnosed with SSc, hospitalized in a university clinic in Bucharest was included in an observational study. The evolution of digital ulcers was evaluated as an indicator of vasculopathy and their status and dynamics were correlated with clinical elements reflecting the fibrotic aspect of the disease. The present study shows that the Raynaud phenomenon is almost always present during the course of the disease, but its presence is not always associated with digital ulcers. The existing data in the literature show that fibrosis is subsequent to vasculopathy, but this study did not reveal causality between these two aspects of pathogenesis. The presence of microstomia and digital contracture was identified in the presence of digital ulcers, but also in their absence. The etiopathogenic mechanisms with multiple unknown involved factors open the opportunity to investigate many aspects of SSc for optimal aiming of therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: Raynaud's phenomen; digital ulcers; microangiopaty; microstomia; microvasculopathy; systemic sclerosis.
Copyright: © Bobeică et al.
Figures
References
-
- Butt SA, Jeppesen JL, Fuchs C, Mogensen M, Engelhart M, Torp-Pedersen C, Gislason GH, Jacobsen S, Andersson C. Trends in incidence, mortality, and causes of death associated with systemic sclerosis in Denmark between 1995 and 2015: A nationwide cohort study. BMC Rheumatol. 2018;2(36) doi: 10.1186/s41927-018-0043-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friedrich S, Lüders S, Glimm AM, Werner SG, Schmittat G, Burmester GR, Backhaus M, Riemekasten G, Ohrndorf S. Association between baseline clinical and imaging findings and the development of digital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(96) doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1875-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
