INHBA knockdown inhibits proliferation and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma SUNE1 cells in vitro
- PMID: 32509056
- PMCID: PMC7270653
INHBA knockdown inhibits proliferation and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma SUNE1 cells in vitro
Abstract
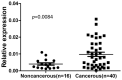
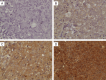
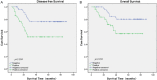
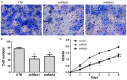
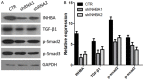
Up-regulated expression of INHBA has been reported in multiple malignant tumors. However, in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), the expression pattern and clinical significance of INHBA are still unclear. This study aimed to detect the expression of INHBA and its prognostic significance in NPC, then explore the tumor-associated functions of INHBA gene and the potential mechanism. The INHBA expression of mRNA levels in tumor tissues and noncancerous nasopharyngeal tissues was investigated by RT-qPCR. The protein expression in cells were detected by western blot. Cell proliferation was detected by CCK assay and cell invasion ability was evaluated by Transwell assay. The expression of INHBA in paraffin-embedded NPC tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Statistical analyses were further applied to assess the clinical significance of INHBA expression. The result reveals INHBA mRNA level is elevated in NPC tissues compared to those in noncancerous nasopharyngeal epithelial tissues. In paraffin-embedded NPC tissues, immunoreactivity of INHBA was primarily detected in 53.70% (58/108) of these patients. The overexpression was notably associated with the clinical stage (UICC) (P=0.048), N classification (P=0.042), carotid sheath involvement (P=0.016), and decreased disease-free survival (DFS) (P=0.004) and overall survival (OS) (P=0.010). Multivariate analysis revealed that INHBA expression was an independent prognostic factor for DFS (P=0.028). CCK assay showed SUNE1 cells' proliferation was decreased in INHBA knockdown group than control. Transwell assay showed the invasion of SUNE1 cells was decreased in INHBA knockdown group by comparison with control. Further study showed knockdown of INHBA expression in SUNE1 cells could block the TGF-β signaling pathway. In conclusion, INHBA is up-regulated in NPC, and is significantly correlated with clinical stage (UICC), N stage, carotid sheath involvement, and survival. Knockdown INHBA in SUNE1 cells could inhibit the cells' proliferation and invasion. The underlying mechanism may be blockade of the TGF-β signaling pathway.
Keywords: INHBA; NPC; invasion; prognosis; proliferation.
IJCEP Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The expression status of ZIC2 as a prognostic marker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Sep 1;11(9):4446-4460. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949842 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of chromosome 14 open reading frame 166 correlates with disease progression and poorer prognosis in human NPC.Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(10):7977-86. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3518-8. Epub 2015 May 12. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25964093
-
APLNR is involved in ATRA-induced growth inhibition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and may suppress EMT through PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling.FASEB J. 2019 Nov;33(11):11959-11972. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802416RR. Epub 2019 Aug 13. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31408612
-
Downregulation of EB virus miR-BART4 inhibits proliferation and aggressiveness while promoting radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Dec;108:741-751. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.146. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30248542
-
Along with its favorable prognostic role, CLCA2 inhibits growth and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via inhibition of FAK/ERK signaling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Feb 20;37(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0692-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29463274 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
INHBA gene silencing inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by repressing TGF-β signaling pathway activation.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Nov 8;18(1):848. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04330-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37940978 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibin βA is an independent prognostic factor that promotes invasion via Hippo signaling in non‑small cell lung cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Nov;24(5):789. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12429. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34505633 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of INHBA as a potential biomarker for gastric cancer through a comprehensive analysis.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 1;13(1):12494. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39784-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37528145 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA 0000654 facilitates the growth of gastric cancer cells through absorbing microRNA-149-5p to up-regulate inhibin-beta A.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):469-480. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2009414. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35100076 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibin subunit beta A promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):11567-11575. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1971028. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34889158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wee JT, Ha TC, Loong SL, Qian CN. Is nasopharyngeal cancer really a “Cantonese cancer”? Chin J Cancer. 2010;29:517–26. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Yu WM, Hussain SS. Incidence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Chinese immigrants, compared with Chinese in China and South East Asia: review. J Laryngol Otol. 2009;123:1067–74. - PubMed
-
- Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP, Chan ATC. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2016;387:1012–1024. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
